14 Alternatives To Buying A New GPU When You Want A Better Frame Rate
If you're a tech enthusiast as well as a PC gamer, you might be one to chase a high frame rate even on the most GPU-intensive games on the market. After all, a higher frame rate often results in a more enjoyable gameplay and can even provide an advantage when playing competitive games. One of the simplest ways to achieve a higher frame rate when gaming is to use a better GPU, coupled with a well-optimized gaming monitor. However, a powerful new GPU is really expensive, so much to deter potential PC builders or existing users who plan to upgrade to a better graphics card. However, not all is lost.
There are numerous workarounds, hacks, and practices you can follow to achieve a higher frame rate and enjoy smoother gaming while making do with the GPU you already have. Those tricks can occasionally be annoying to work with, but they can save you hundreds and hundreds of dollars while still upgrading your gaming experience. Here are some of the most effective alternatives to buying a new GPU for better frame rates when gaming.
Overclock your current GPU
Overclocking your GPU involves pushing its clock speed beyond the default settings. This is done to extract better performances, which can significantly boost frame rates in certain games. With increased core clock speed, the GPU can process graphical data faster, rendering frames more quickly. If you decide to overclock your GPU, you can use tools like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X1, depending on your graphics card's brand. These allow you to make precise adjustments through a user-friendly interface.
To overclock your GPU safely, you need to have adequate cooling in place. Higher clock speeds generate more heat, so it's vital to monitor temperatures using software like HWMonitor, too. Overclocking also requires a stable power supply to avoid crashes. Once you overclock, the performance gain is most noticeable in GPU-bound games, where an old graphics card can be a performance bottleneck. In titles like these, overclocking can smooth out frame drops during high-demand scenes. However, results can vary based on the GPU model, and older cards may have less headroom than newer ones. It's also advisable to check manufacturer guidelines, since overclocking may void the warranty of your GPU. If you decide to go ahead, it's worth noting that an overclock between 5% and 15% can yield an improvement of five to 10 FPS, depending on the GPU model and game demands.
Update your GPU drivers
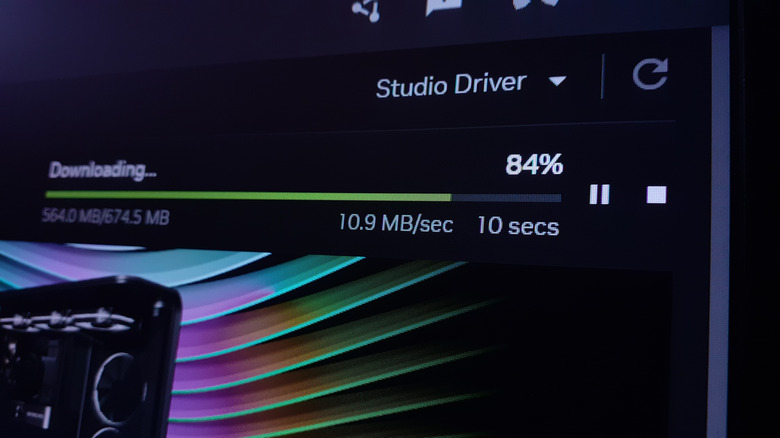
What enables the communication between your graphics card and the game you're playing are the GPU drivers, which is why it's important to keep them regularly updated. Outdated drivers can hinder performances and cause stuttering or low frame rates. Manufacturers like Nvidia, AMD, and Intel release regular driver updates to optimize performances for new games, fix bugs, and improve efficiency. You can download those updates from the manufacturer's website, but the easiest way to get them is to use tools like Nvidia GeForce Experience or AMD Adrenalin, which automatically detect which drivers you need to install, too.
New drivers often include game-specific profiles that adjust settings for optimal performances, reducing frame drops in demanding scenes. For instance, Nvidia's DLSS and AMD's FSR can enhance frame rates in compatible games by upscaling lower resolutions, and support for newer games is constantly added with new drivers. Keeping drivers updated also ensures compatibility with modern APIs like DirectX 12 or Vulkan, which are critical for newer titles. The whole process only takes a few minutes, making it one of the simplest ways to improve frame rates. Check for updates every few weeks to ensure you're not missing out on performance gains, especially after major game launches. Usually, you can turn on automatic updates so that you're notified every time there's one available for your GPU.
Optimize in-game settings
Every game is unique. Some may have pre-recorded scenes and a story mode, while others may have more demanding elements within the gameplay. So, it's important to play around with the in-game settings for every individual game you play. High settings like ultra textures, ray tracing, or maxed-out shadows are heavily taxing on your GPU, reducing frame rates. By lowering settings such as texture quality, shadow detail, antialiasing, or ambient occlusion, you can reduce the GPU's workload, which lets it render more frames per second.
Start by identifying GPU-intensive settings, ideally using the in-game benchmarks, if the title has one. Shadows, lighting effects, and render distance are often the ones behind low FPS. Turning off motion blur can also help in some cases. Many games offer presets, like low, medium, high, etc., that balance visuals and performances. If you're unable to decide which settings to change manually, you can toggle between these presets to find one that delivers the best of both worlds: decent visuals and high frame rates. Alternatively, you can also look for recommended settings on fan forums or Reddit communities.
Enable high-performance mode
If you're using a Windows laptop, you're probably aware of the different energy modes Windows 10 and 11 provide. Within them, the High-performance mode — accessible via Windows Power Options — prioritizes CPU and GPU performance over energy efficiency, ensuring your hardware runs at full capacity. This can prevent frame drops caused by power throttling. Notably, your laptop needs to be plugged into a power outlet for the change to take place.
Closing background apps before launching a game can also make a noticeable difference. Software like web browsers, Discord and Slack, or streaming apps like OBS, consume CPU, RAM, and sometimes GPU resources, lowering performances. Use the Windows Task Manager to identify and close resource-hogging processes before gaming. For instance, Chrome can use one or two GB of RAM when multiple tabs are open, reducing the memory available for your game. Disabling unnecessary startup programs via the Task Manager's 'Startup' tab can also help. On systems with limited resources, this can improve frame rates and reduce stuttering and input lag.
Expand your PC's RAM
Insufficient RAM can bottleneck your system, causing frame rate drops and stuttering. Modern titles like Baldur's Gate 3 or Cyberpunk 2077 often require 16 GB of RAM or more for smooth performances. If your system has 8 GB or less, upgrading to 16 GB or 32 GB can significantly improve frame rates by reducing reliance on slower virtual or swap memory, which lives on your HDD or SSD. When the RAM is insufficient, the system swaps data to the drive, slowing down texture loading and frame rendering, especially in open-world games.
Adding RAM to your PC is straightforward: purchase compatible modules as per your motherboard's DDR type and speed, and install them in available slots. Dual-channel RAM configurations, like two 8 GB sticks instead of a single 16 GB one, double the memory bandwidth, further enhancing performances. This is a cheap way to increase your PC's power, since even the best RAM brands will sell you a 16 GB (2x8) set for $50. While installing RAM is an easy step if you have a desktop computer, it's slightly more challenging with a laptop. Some laptops come with the RAM stick soldered to the motherboard. If that's your case, then sadly, you won't be able to upgrade your RAM. That said, many of the best PC brands for laptop gaming often have replaceable RAM in their machines.
Upgrade to a faster SSD
A slow storage unit can impact your PC's gaming performances just as much as a small RAM stick can. A fast SSD may not directly boost frame rates, but it can certainly make the game smoother by reducing load times, rendering textures faster, and generally improving performances. All of these factors combined can elevate the overall gaming experience. Traditional HDDs or slower SATA SSDs struggle with modern games that stream large assets in real-time. Upgrading to a high-speed NVMe SSD, like a PCIe 4.0 with read speeds above 5000 MB/s, ensures faster access to data.
For example, an NVMe SSD can reduce stuttering in open-world games by quickly loading textures and geometry, allowing the GPU to focus on rendering rather than waiting for data. If your system lacks an M.2 slot, a SATA SSD is still a significant upgrade over an HDD. Make sure to install your OS and games on the SSD, or you won't gain as much of a benefit from it. Even the best major SSD brands have started making their storage devices quite affordable, making this a cheap way to improve performances.
Use resolution scaling
Resolution scaling reduces the in-game rendering resolution while maintaining your monitor's native display resolution, significantly boosting frame rates. For example, rendering a game at 80% of 1080p reduces the GPU's pixel workload substantially, potentially increasing frame rates in demanding games. Technologies like Nvidia DLSS, AMD FSR, or Intel XeSS use AI or spatial upscaling to make lower resolutions look sharper. This can bring to life beautiful visuals at scaled-down resolutions, resulting in a good mix of performance and aesthetics.
Most modern games include resolution scaling sliders in their settings, but you can also enable DLSS/FSR if your GPU supports it. For older GPUs without these features, manually lowering the resolution via game settings or driver software achieves similar results. This method is particularly effective for mid-range or older GPUs struggling with high resolutions like 1440p or 4K. The trade-off is a slight reduction in image sharpness, but you might decide that the smoothness makes up for it. Since the resolution can be adjusted on each game individually, you don't have to scale it down if you're playing a title that runs well natively.
Cap the game's frame rate
While many gamers chase frame rates close to 120 FPS, a sustained frame rate of 60 FPS can result in a more consistent experience than a higher but unstable number. This is what frame rate caps are for: limiting the maximum FPS your GPU renders and reducing its workload over long gaming sessions. Uncapped frame rates may push the GPU to its limit, causing inconsistent frame times and stuttering, especially in GPU-bound scenarios.
Use in-game settings or the Nvidia/AMD control panel to set a frame rate cap slightly below your GPU's average performance in a game. You can find what this number is by running the in-game benchmark, if there is one. Regardless, if you have a 60 Hz monitor, you should cap the frame rate no higher than 60, since you won't be able to display more than 60 FPS. The downside of a frame rate cap is, of course, lower maximum FPS, but the improved stability will feel like an overall upgrade to some users.
Clean your PC's fans
Thermal throttling is one of the biggest culprits behind performance issues, leading to frame drops and lag when gaming. Dust buildup on the GPU and case fans reduces cooling efficiency, leading to thermal throttling. In turn, this leads to the GPU lowering its clock speeds to manage heat, which causes frame drops. If you find that your GPU is constantly running at 90 degrees Celsius, there might be a dirty fan to blame for your performance issues. Cleaning fans will restore the PC's airflow, helping to keep temperatures low and maintaining optimal performances.
To safely clean the inside of your PC, start by identifying all the fans on the GPU and in the case. Then, power off your PC, open the case, and use compressed air or a small air duster to remove dust from the fans and heat sinks. You can also use a soft brush to remove larger debris. Try to clean your PC case every few months, especially if it's located in a dusty environment. The process only takes a few minutes, but the results are noticeable. That said, make sure you don't touch any of the components inside the case with your bare hands or when the power cable is connected, since doing so can discharge static electricity, which could damage the components.
Enable adaptive sync on your GPU and monitor
Adaptive sync technologies like Nvidia G-Sync or AMD FreeSync synchronize your monitor's refresh rate with the GPU's output frame rate, thus reducing stuttering and image tearing. While this only improves the perceived smoothness of the image without altering the actual frame rate of the game, it's still a visual boost that many gamers will appreciate. For example, if your frame rate is oscillating between 40 and 60 FPS, adaptive sync will make the gameplay feel closer to a consistent 60 FPS. It will also eliminate visual artifacts, especially on mid-range GPUs struggling with modern titles.
The only drawback of this technology is that you need both your GPU and your monitor to support the same adaptive sync system, be it G-Sync or FreeSync. If your monitor supports your graphic card's preferred system, you might have to activate it on both the display's internal menu and the GPU's software. To check if your monitor supports G-Sync or FreeSync, reference the instruction manual or the manufacturer's website.
Use a monitor with a lower resolution and refresh rate
A monitor with a lower refresh rate does not inherently reduce the GPU's workload. However, if you're targeting a frame rate of 60 FPS or lower, there is no reason to buy an expensive 144Hz monitor, since you will never hit the high frame rate it's capable of. The same logic also applies to monitors with higher resolutions. The fewer the pixels, the easier it is for the GPU to render them in real time. This doesn't mean you should go and buy an inferior monitor compared to the one you already have. If you own a high refresh rate monitor, you can cap the refresh rate in its OSD or in the driver settings to 60Hz or 75Hz.
Doing so will lower the performance target, reducing stuttering and allowing smoother gameplay on older GPUs. The trade-off is less fluid motion compared to high-refresh-rate displays, but that might not be a big issue for you. If you're in the market for a new monitor, you can save quite a bit of money by going with a 1080p/60Hz display, which is more affordable than a 4K/144Hz one.
Upgrade the CPU
A slow CPU can bottleneck your GPU, limiting frame rates in CPU-intensive games. Upgrading to a faster CPU with more cores or higher clock speeds improves game logic processing, physics calculations, and draw calls, allowing the GPU to render frames more efficiently. Even a relatively small upgrade, like going from a quad-core Intel i5-6600K to a modern six-core i5-12400, can boost the frame rates significantly. It's extremely important you check your motherboard's socket and chipset compatibility before investing in a new CPU, lest you buy one that is incompatible.
Upgrading your CPU will undoubtably be more expensive than upgrading the RAM or swapping out a mechanical drive for an SSD. However, processors are usually cheaper than graphics cards, and they benefit the overall system performance. Plus, if you eventually manage to increase your budget and decide to upgrade the GPU as well, you will find yourself with the necessary CPU to support it already installed.
Look for a used GPU
With new GPUs being so pricey, you might be thinking of turning to the used or refurbished market for affordable options. Buying a used, modern GPU with all the VRAM you need from a reputable seller is a cost-effective way to boost frame rates without paying exorbitant prices. For example, a used RTX 2060 is much cheaper than a new GTX 1060, and will usually reach higher FPS in modern games. Buying from a reputable seller on platforms like eBay or from your local marketplace reduces the risk of faulty hardware. Still, you might want to prioritize a used PC components website with a good return policy, just to be safe.
Before buying a used GPU, try to verify its conditions, usage history, and warranty status. If you're buying from an individual in your city, test the card's performances with 3DMark or a similar software before pulling the trigger. A used GPU can provide you with an excellent price-to-performance ratio, but this approach requires extra research and caution. However, if you're building a PC for the first time or need to stay within a shoe-string budget, it might be your best bet.
Try cloud gaming
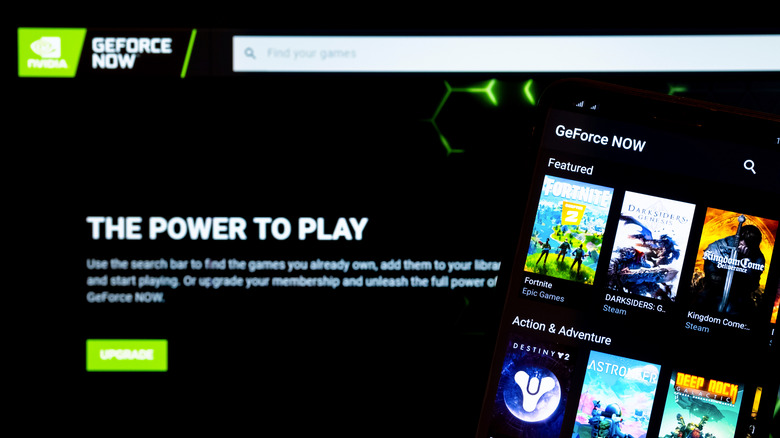
Cloud gaming services like Amazon Luna and its many alternatives stream high-quality games to your PC by relying on powerful remote servers instead of your local hardware. This can deliver high frame rates in modern, demanding titles like Cyberpunk 2077 even on low-end systems, since the rendering doesn't happen on your GPU. GeForce Now's Ultimate tier even offers RTX 4080-level performances, ensuring 120 FPS and more at very high resolutions.
All you need is a stable, high-speed internet connection to minimize latency and maintain smooth gameplay. No hardware upgrades are needed, just a compatible device. The costs are reasonable, too, with GeForce Now's mid-tier subscription coming in at $49.99 for six months of gaming. The trade-off is potential input lag and complete dependency on internet quality, but for gamers with older GPUs, cloud gaming provides access to high frame rates without having to invest hundreds of dollars in new hardware. Another upside is that you can play modern games even on a cheap portable device like a Chromebook.