5 Popular CPUs That Became Outdated In 2025
While it would be nice to have a computer that would last forever, the unfortunate truth is that everything becomes old and outdated. This is particularly true with CPUs, especially as technological advancements mean that once powerful processors lose support and updates from their manufacturer and major software providers.
That's why you shouldn't be surprised to find that some popular CPUs have now become outdated in 2025. This is important to note, especially if you're building your own PC and picking out its first component, to ensure you're not spending money on a system that will soon be or already is outdated.
Note that calling these processors outdated does not mean that they're useless. They often still have a lot of life left in them and could potentially run for many more years. However, they're called obsolete because they either no longer receive the latest drivers that ensure they will work with the latest applications. It could also be that these chips no longer have the hardware capabilities that the latest operating systems require, like Windows 11 and TPM 2.0.
14th-gen Intel Core CPUs with integrated GPUs
Intel launched its 14th-generation Intel Core processors in October 2023, but the company announced in 2025 that it's already putting the integrated GPUs for these CPUs into legacy software support. While this won't affect the processor's performance, and you can still keep on using it as normal, it will no longer receive new features from the chip maker. Instead, it will address only critical fixes and security vulnerabilities and reduce its update support from monthly to every three months. More importantly for gamers, the generation will no longer receive Day 0 Game support, meaning there's a chance that the latest games won't work as smoothly on launch day.
Most users do not need to worry about having this processor in their computer, as it should still work as intended despite the lack of GPU driver updates. This also won't be a problem if you have a discrete graphics card on your gaming PC, as that will take precedence over your CPU's integrated GPU. This move will not affect Intel KF processors, though, because they do not have an iGPU anyway.
This limited support is one of the reasons the top-of-the-line chip from this generation, the Intel Core i9-14900K, is one of the worst CPUs released by Intel and AMD. The 14th-gen Intel Core processors are also affected by an instability issue that caused some high-performance models to fry themselves because of an error in their microcode. The company has since fixed the problem through a BIOS update, but you have to install it manually as it's not included in your typical Windows update.
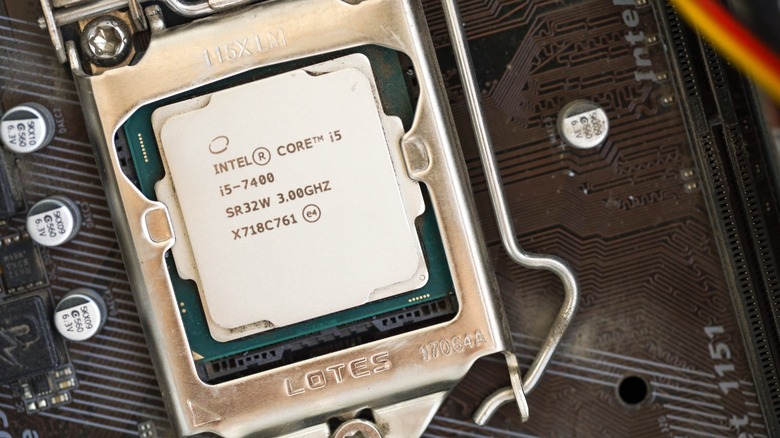
7th-gen Intel CPUs and older
One reason a processor becomes outdated is that it no longer supports modern software features. It's exactly because of this that the 7th-gen Intel Core processor does not support Windows 11, as some models do not have the necessary hardware for TPM 2.0 — a crucial requirement that helps ensure the security of the latest version of the operating system. Aside from this, older chips sometimes lack the necessary drivers to run well with Windows 11, so you might run into unexpected errors that cannot be resolved due to a lack of manufacturer support.
This actually should not be a problem, as these processors should still work well with Windows 10. However, this operating system has already reached end-of-life as of October 14, 2025, meaning it no longer receives updates or support from Microsoft. This can put users who keep using it at risk, as any discovered vulnerabilities will no longer get patched — the primary reason it's time to upgrade to Windows 11.
First-gen AMD Ryzen processors
Intel has dominated the desktop processor market for a long time, but the arrival of Ryzen chips has allowed AMD to gain some ground over its bigger rival. And even though Intel still holds a majority of the market share in desktop CPUs, the company now powers nearly a third of all desktop PCs, and has captured 25% of the overall x86 processor market.
But even though the first Ryzen chips were a game-changer for AMD, their age and advancements in semiconductor and software tech mean that they're no longer suitable for modern systems. These chips arrived in 2017, meaning they're eight years old at the time of writing, virtually ancient in the computing world. More importantly, Windows 11 is not compatible with this processor family, even though it's still quite capable. Given that Microsoft no longer supports Windows 10, that makes them obsolete if you want to stay with Microsoft. However, you can still definitely use them if you switch to Linux instead of Windows 11.
AMD Ryzen 2000 CPUs
Although the AMD Ryzen 2000 family of processors is considered next-generation CPUs to the Ryzen 1000 series, they're still based on the same Zen architecture or the slightly refreshed Zen+. This means that even if these chips are faster and offer better performance than the older processors they replaced, they would suffer from the same lack of features that Windows 11 demands. You can also see this with some Ryzen 3000-series CPUs — Microsoft says that AMD Ryzen 3000 processors (which are mostly based on the Zen 2 platform) are compatible with Windows 11, except for G and GE variants (which are based on the older Zen+ architecture).
Thankfully, since both AMD Ryzen 1000 and Ryzen 2000 processors (and the unsupported Ryzen 3000 G/GE chips) use the same AM4 socket, you can replace them with a newer Ryzen 3000 or 5000 series CPU to install Windows 11 on your system. You just have to ensure that you can update the BIOS on your motherboard to make it compatible with the newer processor, and that it also supports TPM 2.0, which Microsoft requires for its latest OS.
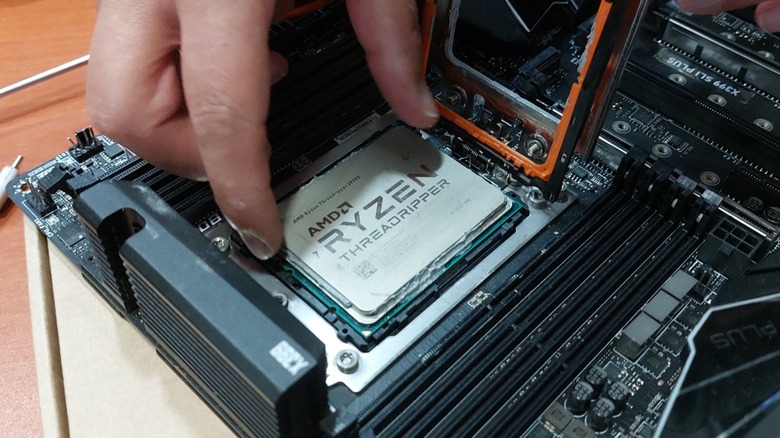
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1000 and 2000 HEDT processors
You might think that specialized HEDT CPUs would have longer lives, especially as they often deliver specifications and performance that mainstream consumer processors can only dream of. But even though they are more expensive and require equally pricey motherboards, they are still not immune to the slow marching forward of time that leads to obsolescence.
Since the Threadripper 1000 and 2000 HEDT processors are both based on the Zen architecture, they are likely to become obsolete alongside their mainstream variants due to a lack of Windows 11 support. But another reason these chips have become outdated is that even AMD has dropped official support for them on the Ryzen Master software. This software is AMD's primary utility for overclocking and controlling AMD CPUs, allowing you to squeeze every drop of performance out of them. The latest version of Ryzen Master will not recognize your processor, so you'll need to keep an older version of this app to tune your CPU — but that also means you're likely missing out on new features from AMD.