5 Ways To 'Speed Up Your Wi-Fi' For Faster Internet
It is nearly impossible to live without the internet today. According to Statista, over 5.56 billion people around the world use the internet daily. Even airplanes now offer in-flight internet at 40,000 feet high. Fun fact: Wi-Fi isn't an acronym for Wireless Fidelity, as some seem to believe. It doesn't actually stand for anything — it was simply coined as a catchy and memorable name, based on the already-in-use Hi-Fi, for high fidelity audio.
While Wi-Fi 7 promises speeds as high as 46GB per second, most of us will get nowhere close to that, since we rely on the (often limited) internet plans we pay for. When the connection feels slow, many of us are quick to blame our Wi-Fi, but the truth is that Wi-Fi is just the facilitator that moves the internet data all around your house. While there are several things in your home that may be ruining your Wi-Fi connection, when most people say they want to "speed up the Wi-Fi," what they really want is a faster internet connection.
However, even shifting to a high-speed data plan may not solve your problem. Many factors, such as an outdated or poorly placed router, can affect internet speed. In this article, we will show you a few smart ways to speed up your Wi-Fi and hopefully improve your connection.
Relocate your router
A Wi-Fi router sends out a wireless signal that allows your devices to connect to the internet, and one of the easiest ways to improve this signal is to place the router close to all the devices that use it. This will help improve internet speed and stability. If your router is surrounded by walls, doors, and other obstacles, the signal can weaken and result in slower speeds or patchy coverage.
However, moving the router to a new location can be a bit tricky, as routers are often installed with a set amount of wiring. Moving the router may require rewiring and help from a technician, especially if you have fiber internet. When choosing where to relocate the Wi-Fi router, favor acentral location so that the signal can reach every room of your house. Try to keep it in an open place where there aren't many obstacles surrounding it, while you're at it.
As for what you shouldn't do, routers aren't supposed to be placed on floors, in the kitchen (or wherever you keep all your appliances), inside cabinets, or close to mirrors. In case relocation isn't possible, you can consider using Wi-Fi extenders or even use your smartphone as a Wi-Fi repeater. This won't improve internet speed in general, but it might give far away devices a solid connection.
Switch to a different channel
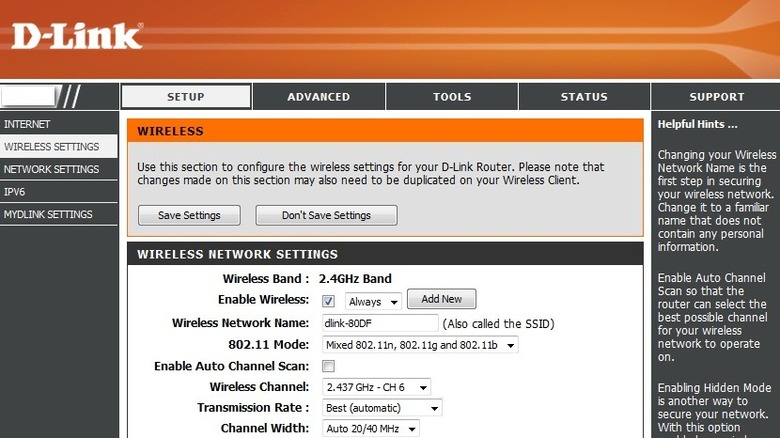
Modern Wi-Fi routers are mostly dual-band and support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. The difference between the two is that, while 2.4 GHz offer wider coverage, the 5 GHz channel will give you the best possible speed, since it transmits data at higher frequencies. The best thing about modern routers is that, if you have a multichannel one, then you can easily switch over to a different channel by connecting to a different Wi-Fi network. By default, most routers distinguish between the two networks with the suffix 2G and 5G.
Different browsers have different configuration pages. Below, you'll find the steps to change the channel for a D-Link router. The steps should appear familiar, even if you're using a different brand.
- Launch an internet browser and enter 192.168.0.1 into the address bar and press Enter.
- Log in into the Admin account.
- Switch to the Settings tab and select Wireless Settings from the side menu.
- Select Manual Wireless Network Setup.
- Disable the Enable Auto Channel Scan option.
- Select a default channel from the Wireless Channel drop-down menu.
Upgrade your router
If you believe that the Wi-Fi router at your home isn't up to the task, then you can always switch over to a new one. There are a lot of affordable Wi-Fi routers on the market that won't put a dent in your pocket. Changing the router is especially important if you've been using an old one that does not offer enough modern features, such as extended range and multichannel options.
Sometimes, you don't even have to buy a new router. Instead, you can call customer support for your internet service provider and ask them to get it replaced. Many service providers change the router periodically so that their service continues to work smoothly. You could even add a second router instead of replacing the one you already have. While you can easily set up a guest network on your existing router, installing a second one can give you an extended reach.
In short, to speed up your Wi-Fi, you need to keep up with the latest Wi-Fi technology. However, that only makes sense if your router is old enough or if your internet plan supports Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7 technology. You could also go for a Mesh Wi-Fi system, but it can be costly when compared to a traditional router.
Upgrade the router firmware
Wi-Fi routers, just like your smartphone, laptop, or TV, have firmware upgrades that add new features and get rid of bugs. However, unlike most other devices, those are unlikely to install updates automatically. Plus, unlike Android, Apple, or Windows devices, your Wi-Fi router manufacturer isn't going to push multiple updates per year.
While some modern routers have the option to automatically update firmware, it is better to check manually if you are troubleshooting a problem. Below are the steps for upgrading the firmware on many popular Wi-Fi router brands:
- Download the latest firmware for your router from the manufacturer's website.
- Open a browser and type 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 into the address bar. A few routers might use a different address.
- Log in to the Admin account. Often, the default username and password are "admin".
- Look for the Firmware Update button, which might be in a sub-menu.
- Click on Browse to load your own firmware and select the file you just downloaded.
- Click Upload. You will soon see a confirmation window where you might need to click Continue.
Remove unnecessary devices
Technically, a Wi-Fi router using IPv4 addressing can handle upwards of 250 connected devices at once, but that is just a theoretical limit based on network standards. In the real world, many consumer routers can handle anywhere between 20 and 50 devices while offering stable internet speeds. However, just because a router can support so many devices, it doesn't mean it can do so without internet speed being affected.
The actual speed on each device depends on a lot of factors, including your internet plan and total bandwidth offered by your service provider, as well as the devices themselves and how much stuff each of them is downloading. Each connected device that is actively using the internet will reduce the bandwidth, which will increase lag in other devices. In such cases, the best course of action is to remove unnecessary devices from your router and free up some bandwidth. Don't worry, you don't need to open the router settings to do this: turning off the Wi-Fi on the devices should be enough.