The Ryobi Timeline: A Closer Look At The History Of Ryobi Tools
For eight decades, the Ryobi brand has produced countless innovations across industries. Despite its humble Japanese origins, it's no wonder that it is now a global household name in more ways than one. Although not necessarily regarded to be as durable as other brands, Ryobi power tools have been known for mostly favorable reviews. Because of their performance and price range, Ryobi power tools are loved by pros and novices alike.
From its cordless drills to soldering pens to air compressors, Ryobi offers products that generally work for straightforward, everyday tasks. Whether you are working on vehicles, kitchen remodeling, or landscaping, there's likely a Ryobi power tool that will help with the job.
However, Ryobi didn't actually start out selling power tools. Here's a look at its history, various owners, and where it might be headed in the years to come.
The origins of Ryobi (1940s)
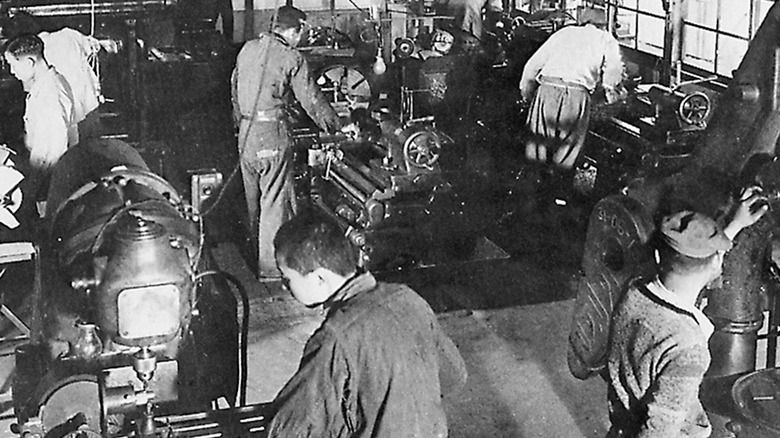
In September 1943, the manager of Mitsubishi Electric's Fukuyama Works in Hiroshima, Japan, proposed the possibility of die casting to Yutaka Urakami. At the time, Yutaka was operating a small trading company and knew nothing about it. However, within a week of this conversation, Yutaka rose to the challenge.
Die casting, according to Ryobi, "is a metal casting process that involves feeding molten nonferrous alloys into dies under high pressure and at high speed to rapidly create molded products." In December 1943, Ryobi, then called "Ryobi Seisakusho Co., Ltd." was established in Hiroshima, Japan. After two months, Ryobi held an opening ceremony for the company, wherein it began manufacturing these products in a retro-fitted soy sauce warehouse and selling them.
Here, Ryobi was able to mass produce thin, complex products, which created smooth casting surfaces that required less machining after being molded.
Among its most popular products, were Ryobi-made automobile industry components. Some of its examples of die casts for cars include cylinder blocks, transmission cases, and shock towers. Ryobi claims that the die casts it produce contribute to the overall weight reduction of vehicles, which is a key aspect that helps improve overall fuel efficiency. After a decade of creating metal die cast products, Ryobi began manufacturing plastic die cast products in 1954.
Ryobi enters the power tools market (1970s)
In 1961, Ryobi became a publicly traded company on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. That same year, it also began manufacturing offset printing presses and later merged with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Machinery Systems, Ltd. It became RYOBI MHI Graphic Technology Ltd. in 2014. Afterward, it expanded its operations across a variety of industries, such as builder's hardware, fishing tackles, and an insurance agency. To make its name simpler and easier to remember, Ryobi Seisakusho was renamed to Ryobi Limited.
In 1968, Ryobi unlocked one category that helped make it a household name worldwide: power tools. From budget-friendly to expensive products made for heavy-duty work, Ryobi amassed a huge portfolio of power tools for both casual and professional users. In 1996, Ryobi launched the cordless lithium-ion technology, the RYOBI 18V ONE+ System, which is still being used until today and features over 280 innovative compatible products.
Unfortunately, as Japan experienced economic decline in the 1990s, the power tools business came under fire. To keep the company afloat, Ryobi announced its Sound Management Plan, a policy that helped reform unprofitable businesses and focus its resources on areas of strength. To do this, Ryobi planned to reduce its workforce, axe its golfing goods, and fishing tackle businesses, as well as sell most of its overseas power tool business.
Ryobi's changing ownership
By 2018, Ryobi decided to execute a company split, which established the Kyocera Corporation, a new company specifically aimed at its power tools business in Japan, Asia, and Africa. Aside from transferring 80% of its shares, Ryobi also turned over all operations related to it, including a manufacturing plant in China and 48 sales office in Japan.
In North America, Techtronic Industries Co., Ltd. (TTI), a Hong Kong-based company, has handled the manufacturing and distribution of Ryobi products since August 2000. By 2002, TTI acquired Ryobi's power tools business in Europe, Australia, and New Zealand as well. TTI's brand portfolio also includes other powerhouse brands like Milwaukee, AEG, Empire, Hoover and more. In 2022, TTI claimed to have generated $13.3 billion in annual sales across its portfolio.
In 2023, Home Depot named TTI's two brands, Milwaukee Tool and Ryobi, as Partner of the Year under three different categories. In a press release, it also shares that Ryobi Outdoor Power Equipment was one of the finalists of the 2023 Innovation Award. It was the first time in the award's history that a supplier has won three Partner of the Year awards in a single year.
The state of Ryobi power tools today
In 2023, Yipit Data claims that Ryobi has led the outdoor power equipment industry with a 20% market share for the past two years. In the United States, Yipit Data also notes that Ryobi's power tool brand share for Home Depot made up 35% of its total sales in Q4 2022.
With this, it's no wonder that the World Tool Awards hailed the Ryobi cordless nailer R15GN18 as the winner of its Premium class of Cordless Nailers category in 2022. A year later, Ryobi also snagged 9 wins at the 2023 Pro Tool Innovation Awards, including cordless power tools: the Ryobi 18V ONE+ 1800W Power Station RYi818BG for inverters over 1000w and the 18V ONE+ HP Mud Mixer PBLMM01B mixer.
And, it looks like Ryobi has no intention of slowing down. In 2023 alone, Ryobi introduced 17 new products to its line up, which include compact cutting tools, cordless blowers, and hedge trimmers. It also unveiled the new Ryobi 80V Power Source, which works in tandem with existing Ryobi 80V batteries and can provide up to 1000 watts of power on the go.