Cadillac V2V Goes Live: What You Should Know About "Talking Cars"
Cars that talk among themselves are the future of road safety, and Cadillac is rolling out its first Vehicle-to-Vehicle communications system today. The 2017 Cadillac CTS will be the first of the automaker's models to get the so-called V2V technology, a special radio which allows cars to communicate when they're within around 1,000 feet of another so-equipped car. While the possibilities of V2V have been tipped as instrumental in autonomous driving one day breaking into the mainstream, for now Cadillac's implementation focuses on safety.
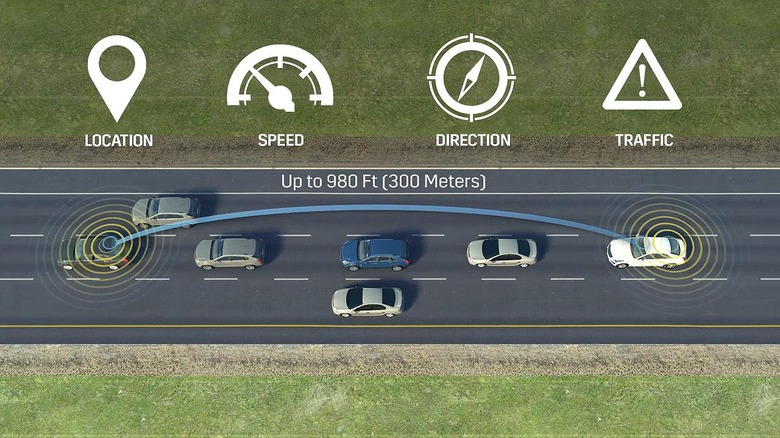
The system can broadcast the CTS' location, speed, direction of travel, and details on traffic conditions around it. That might not sound like much, but it's enough to form a pretty solid perspective of the real-time road activity. In effect, Cadillac says, it's like being able to see around a blind corner ahead.
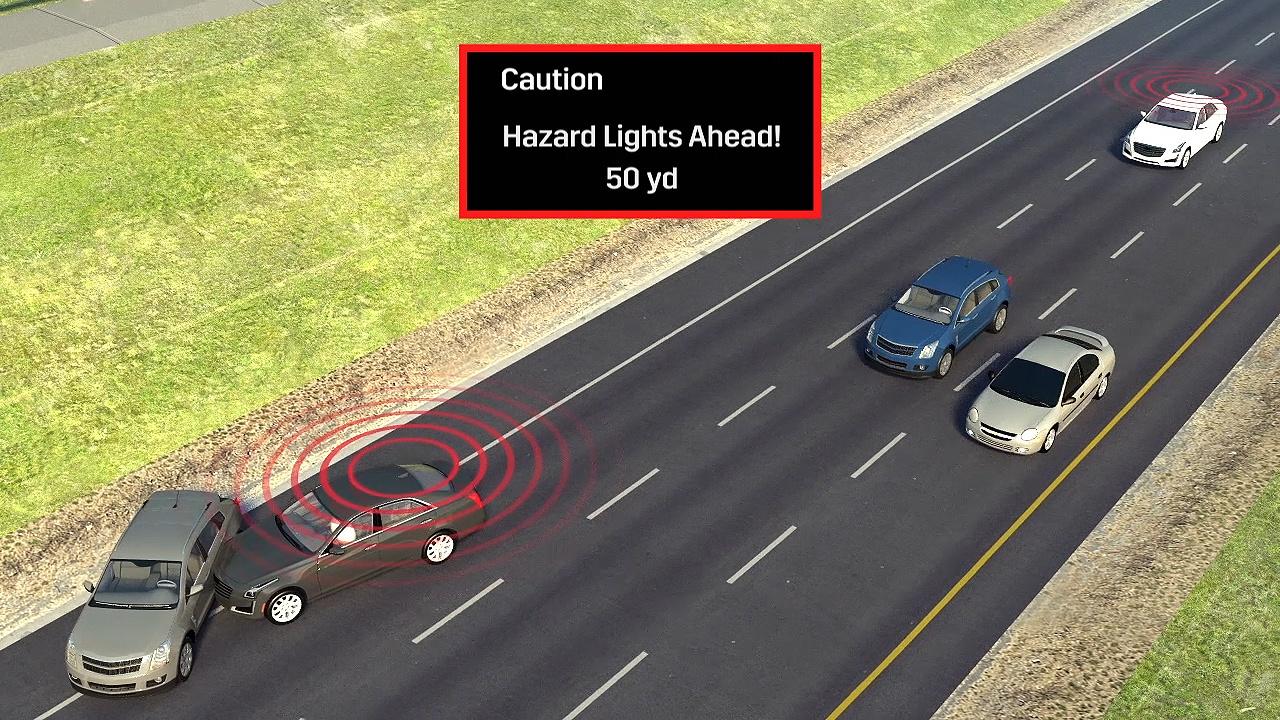
So, if a CTS ahead has to slow suddenly because of an obstacle in the road, or unexpected stopped traffic, that can be broadcast as a warning. V2V-equipped cars further back down the road can receive that alert, and flag up a message on the CTS' digital dashboard display to give the driver a heads-up of the conditions. The wireless technology has a range of under 1,000 feet, and when multiple V2V-equipped cars are in proximity they can automatically create ad-hoc networks.
Cadillac is using the 5.9 GHz wireless band, which the FCC has assigned for "intelligent transportation systems" moving forward. [Update: An earlier version of this article suggested multiple interlinked CTS could in effect create a mesh network, passing safety messages throughout. Cadillac tells us that is not part of the current system.]

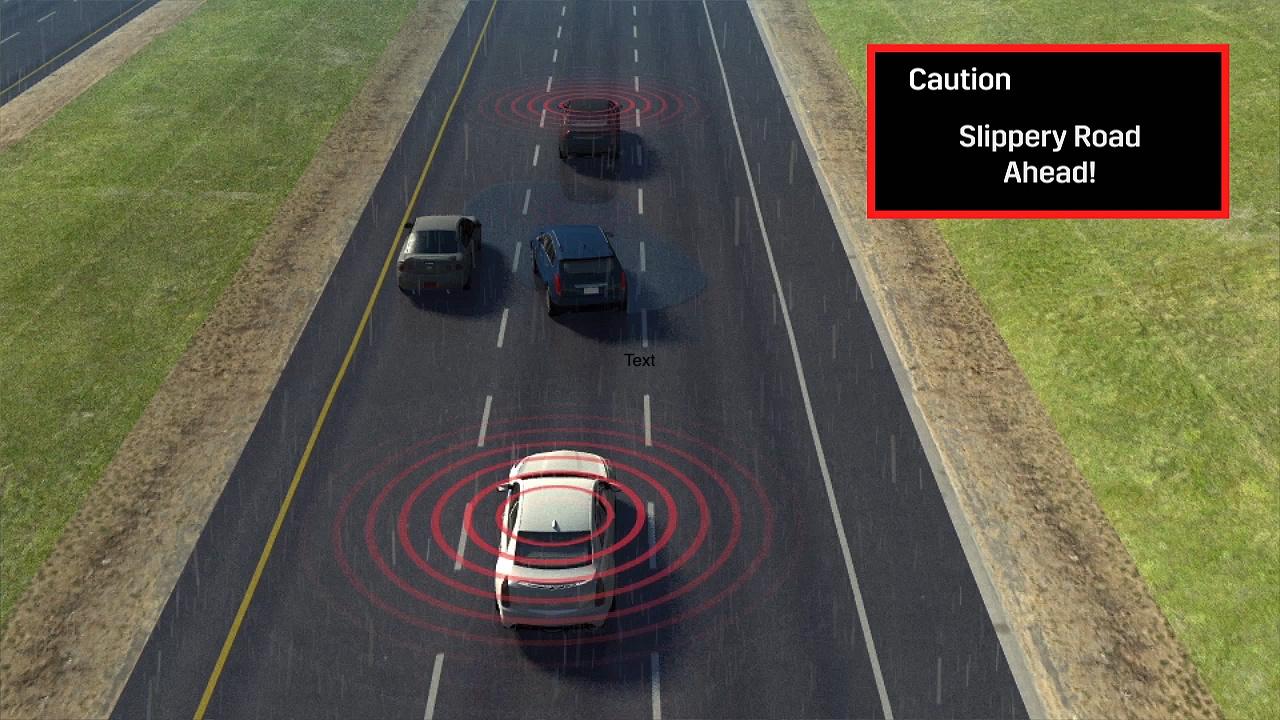
Other possible warnings the V2V system could broadcast beyond just hard braking are disabled vehicles. That might be a crash in the road, or just a stopped truck doing maintenance work in the nearside lane. Cadillac's system would be able to report that back to other cars, giving their drivers advanced notice. Similarly, slippery conditions could be flagged up before the car actually reaches them.
The combination of GPS and Dedicated Short-Range Communications, or DSRC, is able to handle receiving 1,000 messages per second from other vehicles. Since only a fraction of vehicles will have V2V technology initially, Cadillac's system won't just be focused on what the CTS itself is doing. As it reaches intersections, for instance, it will be actively scanning the area for other vehicles and their movements.

Cadillac's next-generation user-experience infotainment system, which is also making its debut on the 2017 CTS, will allow notifications and alerts to be customized according to how much the driver wants to see. If they have the head-up display fitted, those warnings can also be shown there, overlaid atop the road ahead. Best of all, it won't be an expensive option, with Cadillac electing to fit it as-standard across all 2017 CTS from this point on.
V2V is part of a suite of next-generation automotive safety tech which a number of players in the industry are experimenting with. Other iterations include V2I, or Vehicle-to-Infrastructure, where the car communicates with the "smart city" around it. An example of that is Audi's connected traffic lights system, currently active in Las Vegas, NV, but set to expand to new municipalities in 2017. That allows a countdown of how long before the upcoming red light changes to green – or vice-versa – to be flagged up on the dashboard of select Audi cars.
The longer game, though, looks to 5G as the tipping point. Although the upcoming technology is best known for its potential increases in speed, it will also introduce a dramatic cut in latency of communications. That's going to be essential for getting near-real-time updates from groups of proximate vehicles distributed, with enough time for human – or AI – drivers to react appropriately. Last month, Qualcomm demonstrated its own take on V2V or Car-2-X, announcing it would begin trials with LG from next year. One of the features Qualcomm envisages is connected road furniture – like lights or signs – acting as temporary beacons, keeping a cache of alerts sent out by cars as they come into range and then rebroadcasting them to other vehicles as they drive by later on.
NOW READ: 2016 Cadillac CTS-V Review
Right now, Cadillac tells us, its V2V system has only been designed to work with other Cadillac cars. However, a spokesperson confirmed to us, as more automakers get onboard with V2V-style technology, Cadillac is open to discussing intercommunication between different platforms. If and when that happens, the possibility of finding an ad-hoc network to join as you head out on the commute should get a whole lot more likely.




