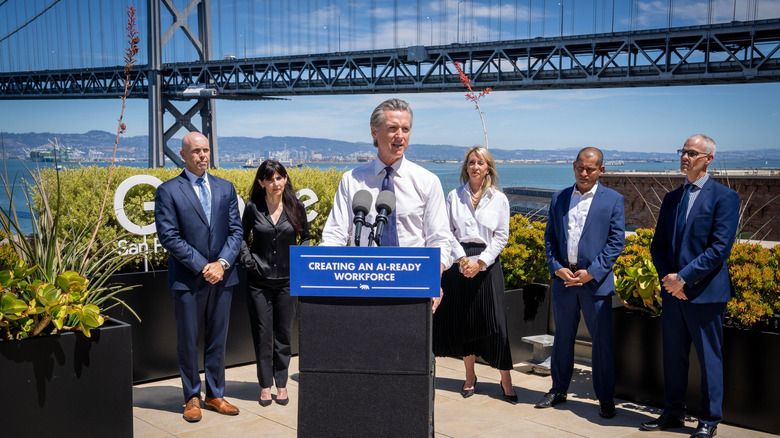
How California Leads The Way Requiring AI Companies To Follow Safety And Transparency Laws
California put itself at the forefront of AI governance with two pieces of legislation, SB53 and SB243, with the potential to shape the history of artificial intelligence. The first establishes transparency rules for the fastest-growing industry in America, requiring that companies publicly cite safety policies and report critical issues. Advocates hope the law will curtail an industry often cloaked in shady disclosure practices, making it easier for companies and whistleblowers to report public safety issues and instilling tangible enforcement mechanisms to hold abuses accountable.
The latter, meanwhile, attempts to protect vulnerable users from the adverse effects of AI companion applications through age verification requirements, disclaimer mandates, and self-harm prevention requirements. The laws come as the debate over AI governance rages across the country, with President Trump promising that the federal government will strike down legislation that limits the sector's growth, and Congressional Republicans attempt to ban states and local governments from curtailing the industry.
Meanwhile, New York is weighing its own Frontier AI law, and several state legislatures aim at regulating companion applications. Age verification laws, content bans, and even potential VPN restrictions further underscore these ethical dilemmas, while the industry's rapid growth necessitates immediate solutions. California is uniquely positioned in this debate. The world's 4th largest economy, the Golden State is a leader in the AI space, hosting 32 of Forbes' top 50 AI firms. According to Stanford's 2025 AI Index Report, 15% of all AI job postings were located in California, while Pitchbook found that more than 50% of venture capitalists' investments in AI went to Silicon Valley. These trends come as no surprise, with AI giants like Apple, Google, and Nvidia based in the state.
A landmark transparency bill
The Transparency in Frontier Artificial Intelligence Act instills basic guardrails for frontier artificial intelligence through 'evidence-based policymaking' that balances transparency, security, and innovation considerations. Building off California's March 2025 working report on the state of AI, the law sets a few basic parameters. To foster transparency, the bill requires developers to publish best practice policies on their websites, ensuring companies live up to industry norms and international standards. The bill also creates a mechanism to hold companies accountable through civil penalties, while making it easier to protect whistleblowers.
To prevent large disasters as AI further ingratiates itself into our public and private infrastructure, companies must report potential safety issues like nuclear meltdowns, biological weapons, or cyber attacks to California's Office of Emergency Services. In addition to safety measures, Senate Bill 53 seeks to foster public-private partnerships through a state-run computing cluster within the Government Operations Agency, dubbed CalCompute, to promote the industry's development.
The new bill isn't the first time California lawmakers have attempted to govern AI. For instance, Governor Newsom vetoed a stricter bill in 2024 requiring AI developers to include shutoff switches, cybersecurity protections, safeguards against 'critical harms,' and safety testing before release. Critics argue that the new bill takes away much of the 2024 bill's regulatory teeth, resorting to mostly voluntary disclosures rather than security requirements to hold companies accountable. Proponents, however, tout the first-of-its-kind law as a blueprint for a federal framework. The industry reaction, meanwhile, has been mixed. Security-minded Anthropic, for instance, publicly endorsed the bill, while Meta and OpenAI initially lobbied against it before silently acquiescing.
Making AI companions safe
In October 2025, California instituted the country's most comprehensive safety measures for AI companions. Senate Bill 243 seeks to protect young and vulnerable users by requiring suitability warnings, AI disclosure notifications, and break reminders for minors. It also mandates new content protocols, requiring companies to prevent chatbots from producing suicide-related content and offer referrals to suicide-prevention resources or crisis lines for at-risk users. Furthermore, SB243 asks providers to prevent companions from sharing explicit material with minors, and companies must publish these protocols on their websites, giving users the 'private right of action' to seek damages against chatbots. Starting in July 2027, AI companions must submit annual reports to California's Department of Public Health detailing their responses to user crises.
The law comes amidst tensions over the influence of AI companions, with a series of lawsuits and investigations implicating companies like Character.AI, Meta, and OpenAI in the wrongful harm or death of minors. Concerns over romantic relationships, inappropriate content, and misleading therapy bots have moved to the forefront as minors become more dependent on the technology. According to a Common Sense Media study, most American teens use AI companions, while the Center for Democracy and Technology found that over 40% used applications for social advice, with nearly 20% admitted that they or someone they knew had a romantic relationship with an AI companion.
These trends will likely continue as AI companions proliferate across social media, with some AI companies even starting their own social media applications. As of 2025, five states have enacted mental health-related regulations for chatbots, though none as comprehensive as California. Whether others follow in the Golden State's footsteps might determine the course of the country's fastest-growing industry.