How Do AI Detectors Work And How Reliable Are They?
Generative AI has made it easier than ever to produce written content. Popular chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok can generate thousands of words on any topic under the sun in mere seconds. Ideally, these chatbots are best suited for generating non-academic content such as emails, letters, notes, or a quick message. However, assuming students won't use such a powerful tool as a shortcut in academic tasks is a stretch. The increasing use of AI by students has left educators struggling to stop the barrage of AI slop in academics.
AI content detectors offer a solution and claim to differentiate between AI and human-written text with a few clicks. Some of these tools also offer text humanizing services that produced lackluster results in our testing. AI detectors are essentially probabilistic models that make a calculated guess about a text by analyzing it for parameters like perplexity and burstiness. That said, flagging AI content is extremely difficult, especially when advanced chatbots are becoming better at their job. There have been multiple cases where human written content has been falsely flagged by such tools. With that in mind, should you really trust the results from an AI detector?
AI detectors work on probabilistic models
Generative AI is trained on massive datasets that helps the underlying model get better at producing text, images, audio, and even videos. Rather than actually thinking and writing like humans, AI models predict the most fitting blocks of words that can satisfy the user's query. These models are further tuned to be extremely polite and formal, while the content they produce is unnaturally smooth and readable. Interestingly, this unnaturalness of AI-generated text also makes it somewhat traceable.
Among other things, AI detectors check a block of text for perplexity, which is the predictability of a thought. For instance, consider 'Colorless green ideas sleep furiously', a sentence coined by professor Noam Chomsky to demonstrate how grammar and semantics don't always go together. Each word in this sentence is completely unrelated to its preceding word, making it a highly perplexing sentence. AI models, on the other hand, naturally generate low-perplexity content. Another characteristic that makes AI-generated content unique is the overall uniformity of sentence length, measured in burstiness. Human-written sentences can greatly vary in length, which differentiates them from robotic content.
AI detectors can be inaccurate
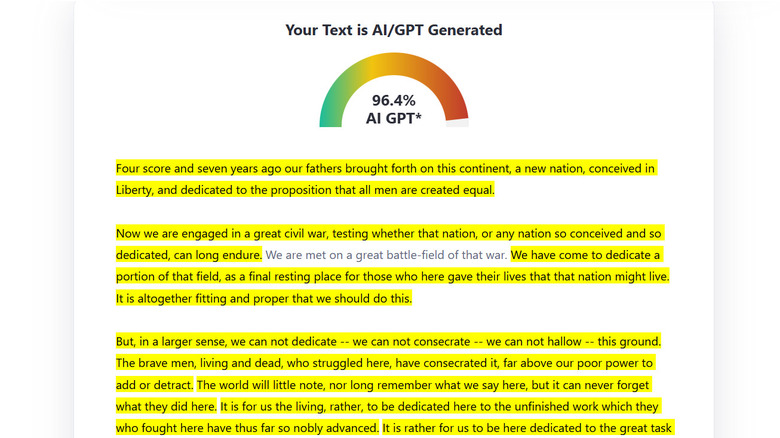
You might have noticed that low perplexity, and to some extent, high burstiness are both signs of good writing. While humans rarely write as unnatural as AI, detectors can flag some human-written text as AI. To test the accuracy of AI detectors, we ran Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address, written in an era when AI wasn't even conceptualized, through three of the best AI detection tools. While QuillBot and Copyleaks AI correctly marked it as human-written, ZeroGPT's AI detector judged Lincoln's speech to be 96.4% AI-generated. Users on online forums like Reddit have echoed a similar problem of false positives with AI detectors.
While running a piece through multiple tools can give some idea about its origins, you cannot trust them blindly. You should manually read through the text and look for clues associated with AI-generated content such as overtly polite grammar and unnatural perplexity. Additionally, AI models are tweaked to avoid direct claims and often use evasive terminology like "It is commonly believed...", "Some might believe...", and more. If you are an educator and have access to the document's history, you may check for any unusually large increments to the word count, that might suggest the use of AI.