Do The Apps Running In The Background On Your Phone Drain Your Battery Faster?
Smartphones have come a long way in the level of convenience they have to offer. You have several instant messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger that let you connect with your loved ones over the internet. Then there's the recent surge of AI-assisted features with nearly every phone release, offering features like smart object removal, accurate transcriptions, and even a way to screen and manage incoming calls for you.
Our phones are also constantly managing and relaying information back to us in the form of notifications. Somebody texts you on iMessage? You instantly get a notification on your iPhone. This is extremely convenient, and honestly, taken it a bit for granted given that the alternative would've been to always leave an app open.
Background app activity is also what allows you to upload large files on Google Drive and switch to another app without pausing or canceling the upload. With the bucketload of notifications your phone receives, it's safe to assume that the majority of the apps on your device have access to background data — but in what capacity? Do all apps drain the same amount of battery when not in active use? Recent versions of Android and iOS make it quite easy to view and manage the apps that run in the background — and here's how you can optimize your phone to stretch its battery life.
Managing background apps on Android
Android largely divides battery consumption based on three states of an app — foreground app when in use, foreground service that isn't visible, and background parts of an app. Phones running Android 13 and newer are equipped with a power consumption tracker that monitors and alerts users if any foreground or background service has been consuming more battery than usual.
Phones running a vanilla Android experience, like Pixel or Motorola devices, will let you view a list of running apps when you pull down to access the quick controls. Here, you can view how long each app in the background has been running for, and stop it with a single tap. You can also view the amount of battery the apps you use have been consuming by navigating to Settings > Battery > Battery Usage. Note that the exact menu names will vary slightly depending on your phone's manufacturer and model.
If you find a service that has been eating way too much of your phone's battery even when not in active use, you can manually revoke an app's access to background usage on Android.
- On your Android phone, launch the Settings app.
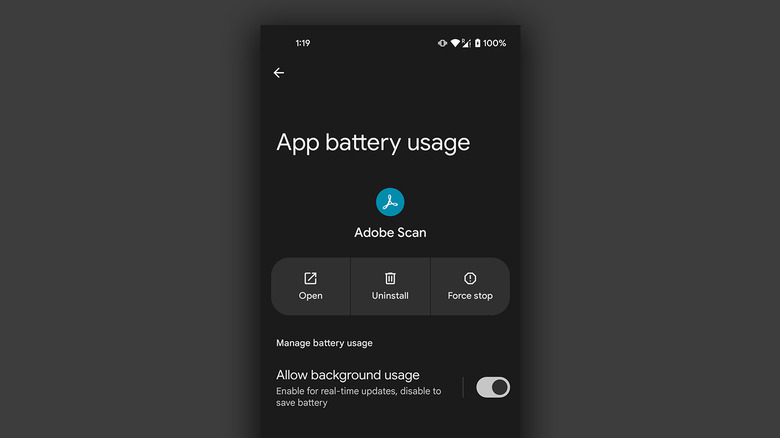
- Navigate to Apps > See all apps, and select the one that has been draining your phone's battery.
- Tap on "App battery usage" and uncheck the "Allow background usage" toggle.
Note that certain services like messaging apps require background activity to function properly and send you notifications in real time.
Managing background apps on iOS
iPhones have generally had a better reputation over the years when it comes to battery management and app performance — but they aren't immune to bad actors that may use excess resources in the background. Unlike Android, iOS doesn't notify its users if an app has been consuming more battery than necessary — but that's not to say that the operating system doesn't have preventive measures in place.
Background services on iOS noticeably run more strictly — which is why you may sometimes get the "open app to finish upload" notification. To view battery consumption on your iPhone or iPad, navigate to Settings > Battery, and scroll down to view a list of apps that have consumed most of your device's battery life in the previous 24 hours. You can also view the amount of time an app has spent in the background and your iPhone's battery health.
If you find a culprit that has been draining way more juice than it needs to, chances are that it has been consuming a lot of resources in the background.
- On your iPhone, launch the Settings app.
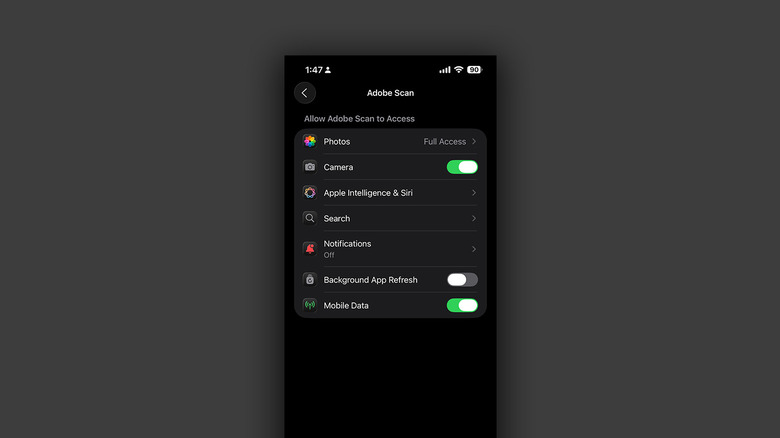
- Navigate to Apps and select the one that has been causing you battery issues.
- Tap the "Background App Refresh" toggle to turn it off.
Once again, this will stop the app from updating information in the background, which isn't ideal if you heavily depend on real-time updates from a service, like navigation or location sharing.