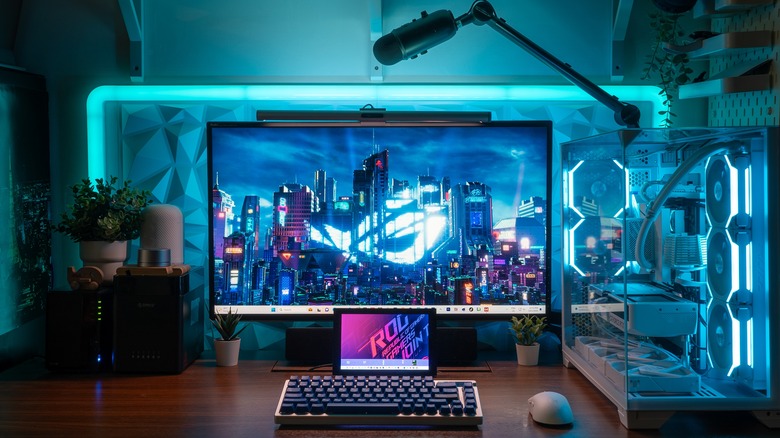
Is It Safe To Overclock A GPU? (And What's The Worst Thing That Can Happen If You Do?)
The practice of "overclocking," specifically in regards to PC components, means to deliberately push a component past its manufacturer-established limits to generate improved performance. In layman's terms, if a particular component is performing at 100% of its capacity, to overclock it would be to push it above that into 110% or even 115% of its capacity. The PC components typically subjected to overclocking are the RAM, CPU, and GPU.
Overclocking your RAM can speed up your PC, and overclocking your CPU can improve your general performance. Meanwhile, overclocking your GPU can increase your PC's graphical processing capabilities, improving the overall speed and quality at which your PC renders complicated imagery. For example, an overclocked GPU could be helpful for running strenuous video games, as it would increase your framerate and cut down on processing lag.
However, you can't push something beyond its established limits without incurring some manner of penalty. Overclocking a GPU in short bursts can give you temporary performance improvements, but if you leave your GPU in that state long-term, the increased heat and power load will cause it to wear out much faster than usual. Additionally, your PC may not be able to keep up with the increased performance, not unlike placing a massive engine into a tiny car.
Overclocking a GPU increases power draw for slight performance improvements
The way overclocking works, physically speaking, is by increasing the processing cycles on a GPU, facilitated through an increased electrical consumption. Let's say your GPU usually performs 50 processing cycles in one second, but you increase that number to 100 in a second. It'd be like if your brain were suddenly capable of processing information at twice the speed it already does. Naturally, you'd be able to figure things out much faster than you could.
Granted, rather than fully doubling the potential, overclocking a GPU will usually only get you performance improvements of around 5-10%, but it's still a tangible boost. By overclocking a GPU, you increase the speed and precision at which the component does its job, generating visual data. If your PC struggles to render a demanding video or game, overclocking may give it the extra muscle necessary to pull itself over the proverbial finish line.
When it's in an overclocked state, your GPU will be able to render high-fidelity graphics on a game with higher consistent framerates and less lag, or more quickly render footage from a video editing program. You can't overclock a GPU from your PC's default interface, but there are many programs and utilities available like MSI Afterburner that can quickly facilitate it. Keep in mind that this does require some technical knowledge and shouldn't be performed carelessly, lest you mess up something important.
Over-relying on overclocking can wear your GPU out faster
The idea of pushing one of your PC's components beyond its established boundaries naturally sounds a little intimidating, and certainly, it's not a process you should undertake half-heartedly. The good news is that overclocking your GPU will not result in any kind of sudden, catastrophic failure like your PC bursting into flames. However, there are still risks. In order to facilitate the overclocking process, you need to increase your GPU's power draw. All that extra processing requires more juice, after all.
The problem is that a GPU is only built to safely endure so much electrical influx. If you push that power draw beyond its limits, the greater electrical consumption will cause the GPU to generate noticeably more heat. Heat is the mortal enemy of safe PC operation, with high temperatures causing your components to wear out quickly. Your GPU won't explode, but expect its overall lifespan to be diminished. It's also worth noting that your GPU is supposed to work in concert with the rest of your PC's components.
If you kick it into overdrive, the rest of your PC might not be able to keep up with the GPU's newly souped-up state. This can lead to unstable performance and glitches, including freezing, crashing, or even data corruption. If you're really set on overclocking your GPU, the best practice is to keep it to short, controlled bursts when you really need that extra power, such as overclocking a gaming PC for competitive play. If you overclock your GPU and leave it that way long-term, your PC will run itself ragged just trying to perform its usual duties.