Are Your Games CPU Or GPU-Bound? Here's How To Check
If you're a professional gamer, you must be aware that every second and move counts in games, especially in online co-op games. If your computer is "just" fulfilling the minimum requirement of the game you're playing, you will experience a lot of stutter and lag, which may eventually cause you to lose the battles and missions in the game. In such a situation, upgrading your system is the best thing to do. But the part of the system that you need to upgrade totally depends on the game you're playing.
If you're playing a CPU-bound game, then it doesn't matter which brand of graphics card you install, whether it's one of the best from Nvidia or AMD; you won't experience any big change in the game's overall performance. In contrast, if you are playing a GPU-bound game, then it doesn't matter whether you upgrade to Ryzen 7 9800X3D or Intel Core i7-14700K; there won't be any noticeable difference in the overall performance of the game. That means it's essential to consider the game you're playing, as well as those you plan to play in the future, before upgrading your system. But exactly how can you determine whether a game is GPU- or CPU-bound? Let's find out.
What's the difference between CPU-bound and GPU-bound games?
It's quite clear by the name itself — a GPU-bound game will heavily rely on the GPU, whereas a CPU-bound game's performance is related to your system's CPU. In a GPU-bound game, your computer's GPU is doing most of the processing, like rendering graphics, textures, and all the other elements of the game. If a game is GPU-bound, you'll need to adjust in-game graphic settings to eliminate lag and stutter, or upgrade your GPU to improve the game's overall performance, such as achieving a better frame rate. Most of the modern, graphic-intensive games like Black Myth: Wukong are GPU-bound.
However, if you are playing a CPU-bound game, then upgrading your computer's CPU will help you get the most performance boost in the game. Just like in GPU-bound games, most of the processing, like physical calculation and element rendering, is done by the CPU in a CPU-bound game. Strategy games like Counter-Strike and Cities: Skylines are some examples of CPU-bound games, where the CPU does most of the complex calculations and manages large amounts of data in real-time.
How to tell if a game is CPU-bound or GPU-bound?
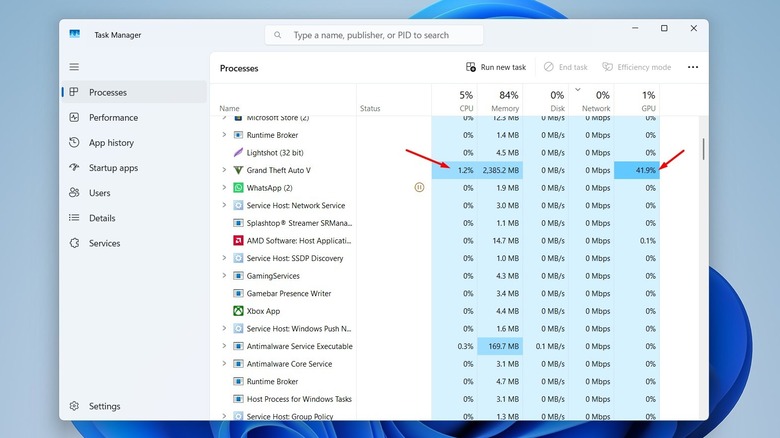
It's pretty easy to determine whether a game is GPU- or CPU-bound. The first way is to use performance monitoring tools like MSI Afterburner or Windows Task Manager and carefully monitor your system's performance while playing the game. For instance, if you're using the Windows Task Manager, check the CPU and GPU consumption numbers next to your game in the Processes tab. If the CPU number for the game is significantly higher than the GPU number, then it confirms that the game is CPU-bound. Whereas if the GPU number is higher, then it means that you're playing a GPU-bound game.
Besides this method, you can also adjust in-game graphic settings to determine the game type. If you start getting a better frame rate after lowering the game's graphic settings, such as shadows and textures, then it's an indication that the game is GPU-bound. However, if you notice little to no difference in the game's performance, it means that the game relies heavily on your computer's CPU for most of the processing and is considered a CPU-bound game.
Interestingly, for most games, you won't even need to perform either of the tests mentioned above to determine its type, as you will be able to tell whether it's GPU- or CPU-bound just by looking at it. If the game features impressive graphics and high-quality textures, it's almost sure to be a GPU-bound game. In contrast, if your game involves a lot of background simulation and NPC interactions, then it's probably a CPU-intensive game.