Why Are Space Launch Vehicles Called Rockets?
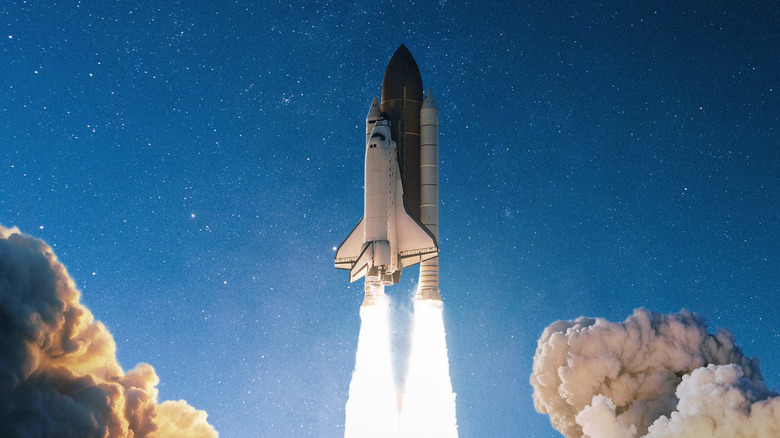
There's truly nothing else like a space shuttle launch. Watching a massive space-faring vessel make its way beyond Earth's atmosphere into the embrace of outer space, in many cases carrying a crew of human beings — one unbelievable NASA concept space shuttle even attempting to carry 86 astronauts — is an astounding sight. At the same time, for as remarkable as space shuttles are, there's some semantic confusion regarding their associated technology. For one, why are the launch vehicles needed to get them up into space known so commonly as rockets?
As it turns out, launch vehicles are known as rockets simply due to the type of propulsion technology they employ. Rocket engines quickly burn fuel, which generates thrust in the form of hot gas. This gas is pushed from the engine, pushing the rocket and its attached space shuttle toward the cosmos. The thrust comes entirely from this reaction and the response of the physical rocket, hence why it's able to so effectively push upward. It doesn't require something to push against, which is entirely lacking in the vacuum of space. As far as why these pieces of machinery are named this way, we can dig a bit deeper.
Rocket engines for space travel are relatively new tech in the grand scheme of human history, though their name doesn't come from a recent source. Rocket technology as a whole has been around for centuries and led to the engine's name.
Rocket technology goes back centuries
Whether it's used for launching space shuttles packed with astronauts or sending missiles across vast distances, rocket propulsion technology may seem like a recent creation. In truth, this form of transportation has existed for centuries, finding its roots in 9th-century China. These early rockets — known simply as "fire arrows" thanks to their flames and attached feathers like a standard arrow — were merely tubes filled with gunpowder, which, when ignited, were swiftly sent forward. These were used for both war and celebration, and in time, they caught on and were developed further in other regions throughout Asia and the Middle East.
Eventually, the tech made it to Europe. In England, monk Roger Bacon tweaked the design for increased range. In France, Jean Froissart added a tube for increased accuracy, while Italian Joanes de Fontana made rockets suitable for naval warfare, designing a surface-running, rocket-powered torpedo — a precursor to the modern SMART missile. As far as recorded uses of the term rocket, those don't arise until long after the technology had become commonplace in various areas. So far, the earliest verifiable use of the word goes back to 1566 in the Christian dialogue "Pasquine in a Traunce" by Italian historian Celio Secondo Curione.
Even though rocket technology has existed for centuries, its ventures into space only began relatively recently. It took some time for hopeful space explorers to adopt it for such a purpose.
When were rockets first used for space exploration?
Evidently, rocket propulsion technology isn't a new creation by any means. Relative to when it was first created, though, its use for space exploration is a recent innovation. Russian schoolteacher Konstantin Tsiolkovsky first proposed the idea in around 1898, going on to suggest in a 1903 report that liquid propellants could send rockets higher than previously seen. By the mid-1950s, the Space Race had begun between the United States and the Soviet Union. As both global superpowers got to work, rocket propulsion technology was brought to the forefront, ultimately being used to great effect.
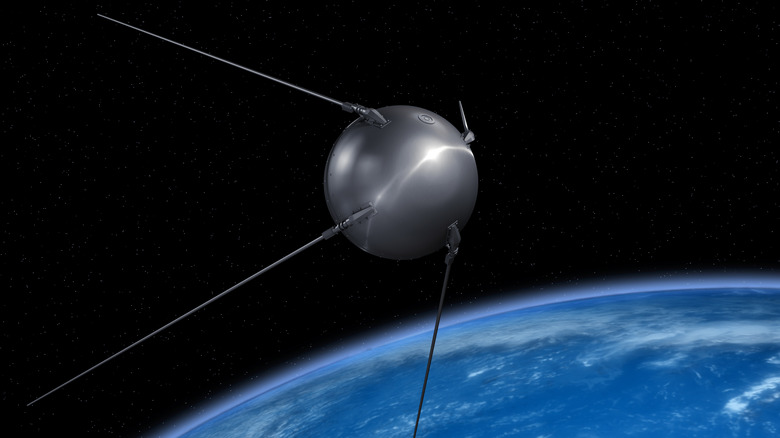
On October 4, 1957, the Soviet Union took a significant step ahead of the United States in their cosmic conflict. The launch of the Sputnik 1 satellite — one of the most important satellite launches in space history, to no surprise — was a success, making the Soviet Union the first to get a satellite into space. Naturally, it didn't just get up there on its own. A 30-meter-tall, 280-ton R-7 rocket was responsible for sending the satellite into orbit. Thus, this marks the first time in human history that rocket technology was used for space exploration, cementing itself as a reliable means of reaching the stars.
What started out as a form of entertainment and warfare on the ground has become humanity's preferred method of space travel. In the coming decades and centuries, it will be interesting to see where rocket propulsion takes us next.