How To Enable Or Disable Fast Startup On Windows 10 Or 11
Fast startup is a handy feature on Windows that speeds up boot times by preventing the PC from shutting down completely. When enabled, it saves part of the system state to a hibernation file on your hard drive during shutdown. Essentially, this feature combines elements of a cold shutdown with hibernation.
Fast startup allows Windows to preload the kernel and drivers, so when you turn your computer back on, it simply refreshes rather than starting from scratch. While this doesn't save your open files or programs like hibernation or sleep mode, it does significantly reduce the time it takes to get your system up and running.
Although fast startup is usually enabled on most Windows computers, you may want to turn it off to fully shut down the system. This guide will walk you through the steps for enabling or disabling fast startup on a Windows 10 or 11 PC and help you decide whether it's the best option for your needs.
How to enable or disable fast startup
The most convenient way to turn fast startup on or off on Windows is via the "Power Options" menu in the Control Panel. To do this, you will need to be using an administrative account on Windows. Here are the steps you need to follow.
- Press Windows + S to open the search menu.
- Type "Control Panel" in the search box and hit Enter.
- Click the "View by" menu in the top right corner to select Large icons.
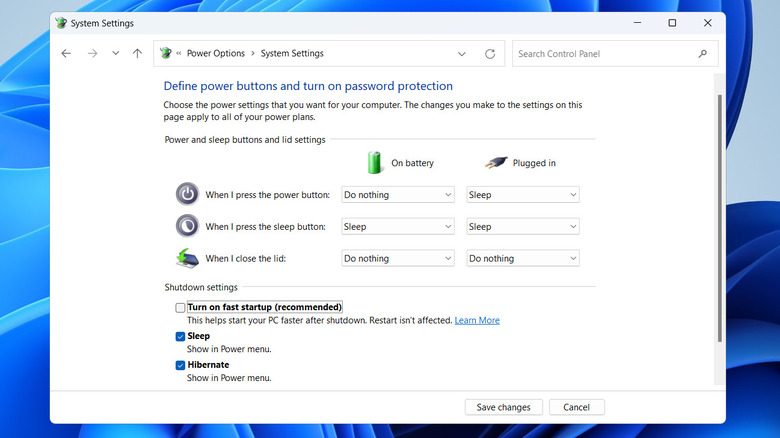
- Go to Power Options and click the "Choose what the power buttons does" option.
- Click the "Change settings that are currently unavailable" option.
- Check the "Turn on fast startup" box to enable the feature, and uncheck it to disable it.
- Click the Save changes button.
If you're comfortable using the Command Prompt, you can also enable or disable fast startup with a simple command. To do so, right-click the Start menu and select either Terminal (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin). In the console, type "powercfg /h on" (without quotes) to enable fast startup and press Enter. To disable it, type "powercfg /h off" (without quotes) and hit Enter.
What to do if the fast startup option is missing
Fast startup relies on Hibernate to function, so if Hibernate is turned off, the fast startup option won't be available in the Control Panel. This issue is more common on lower-end PCs, rather than on powerful Windows computers. To resolve this, you'll need to enable the Hibernate using these steps:
- Click the search icon on the taskbar and type "Command Prompt" in the text box. Then, select "Run as administrator."
- Select "Yes" when the User Account Control (UAC) prompt appears.
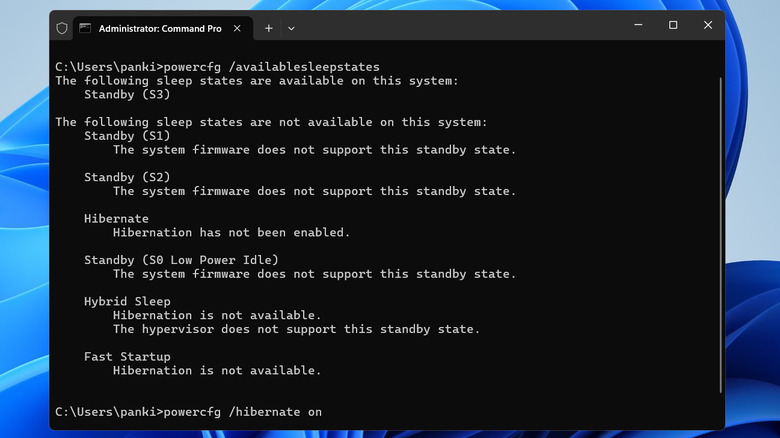
- Type the following command and hit "Enter" to check if your PC supports hibernation: powercfg /availablesleepstates
- You will see the "Hibernation has not been enabled" message if your PC supports the feature. To enable it, type this command and press Enter: powercfg /hibernate on
Once you run the above command, the fast startup option should appear in the Control Panel.
Should you keep fast startup on or off
The fast startup feature is great for those who prioritize speed, but leaving it on has some noticeable disadvantages. Since fast startup prevents your PC from shutting down completely, you might have trouble installing Windows updates at times. Also, if you have a dual boot setup, you may run into issues because Windows locks the hard disk during shutdown. This means you won't be able to access the hard drive from other operating systems.
With fast startup enabled, some computers might not allow easy access to BIOS/UEFI settings after a shutdown. Additionally, if your Windows computer has an SSD, the boot time is already quick, so the advantages of fast startup are less noticeable.
If these drawbacks don't affect you, there's no harm in keeping fast startup enabled, as it does not negatively impact your system's lifespan or performance. Ultimately, whether you should keep fast startup enabled or not depends on your usage and priorities.