Engine Number Vs VIN: How They're Different (And Why It Matters)
Cars these days have seemingly endless options when it comes to customization, from machine-finish alloy wheels through to metallic paints and duo-tone leather interiors, automakers keep on giving us ways to both spend money and personalize our cars. However, most of us have probably been in a situation where a seemingly identical model has parked next or near to us, and we've had to either blip the fob or check the license plates to actually register which is our own.
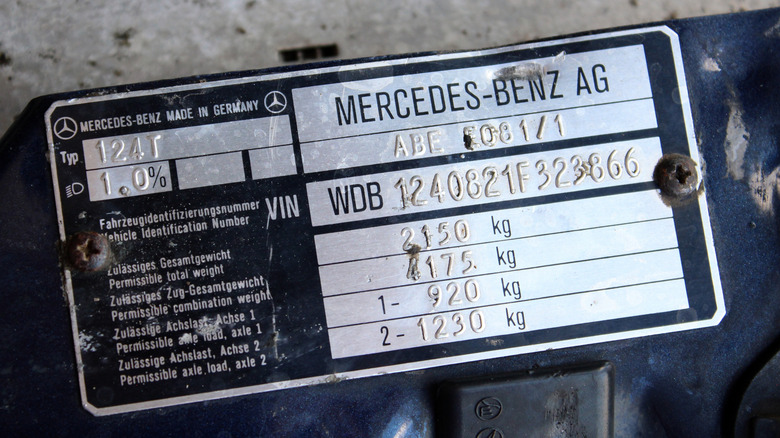
As it happens, there are many more ways to identify your car, as every single model sold sports a unique set of codes, known as the engine code and VIN (Vehicle Identification Number). Although similar, and developed for largely the same purpose, a cars' VIN and engine code are different. Generally speaking, a VIN will be located in one of only a few places, 17 digits long, and it will provide a coded description of what the car is, in addition to further manufacturing details. The engine code, on the other hand, relays information exclusively about the engine, and is particularly helpful to both automakers and part suppliers.
A car's VIN and engine code have to be separate from one another
It might, at first, seem logical to incorporate the engine code within the VIN — or vice versa — but it's actually important that these two codes are kept separate from each other. The VIN is a 17-digit code unique to the chassis. It depicts information such as what the car is — WAU referring to a German Audi, for instance — plus where and when it was produced. The VIN is especially useful for identifying stolen cars, logging insurance claims, and for checking up on any due recalls. Regardless of work carried out on the car, the VIN remains the same, and that's the key fact.
In comparison, a car's engine can be replaced for a multitude of reasons. Some who love to tune and tweak cars may wish to swap in a larger, more powerful engine, such as carrying out an LS swap, while some drivers may have their engine replaced with a like-for-like example if a persistent fault develops. In these instances, the car would then sport a different engine code. If the engine code was part of the VIN, then VIN would then no longer make sense, hence why it's imperative that the two numbers are kept separate from one another.
Engine codes are especially useful when diagnosing or repairing a fault
While the VIN is only ever really useful to most when buying and verifying the identity of a used car, or checking up on recalls, the engine code can be a huge help when it comes to repairs and maintenance. This is because manufacturers are constantly updating and tweaking engines to ensure maximum efficiency and reliability. For example, if an automaker were to tweak the fuel injection system on an existing model, when it comes to replacing injectors further down the line, getting the correct injector for your specific engine could potentially prove to be quite a pain.
Here's where engine codes come in handy. By ordering parts using the full engine code, rather than simply stating your make and model, this would tell the part supplier exactly which revision your engine is. Therefore, they would know exactly which specific part is correct to your engine, rather than simply selecting one of the multiple options available and hoping for the best. Being aware of your engine code can not only help you get parts quicker, but it can also potentially save you money too. Getting hold of the right part quickly gets you back driving sooner, saving on costly diagnostic and/or labor fees.