What Is Mazda's Skyactiv-G And How Does It Work?
The world is changing, and drivers have found their attitudes changing somewhat, too. Perhaps you weren't very conscious of how much gas you were using but are leaning towards more environmentally friendly –- and gas pump price-friendly –- vehicles now.
For their part, manufacturers should recognize this and ensure that such options don't necessarily equate to losing out on power or performance. This is one of the greatest conundrums facing the car industry in the foreseeable future, and Mazda's SkyActiv-G could be an important element of that.
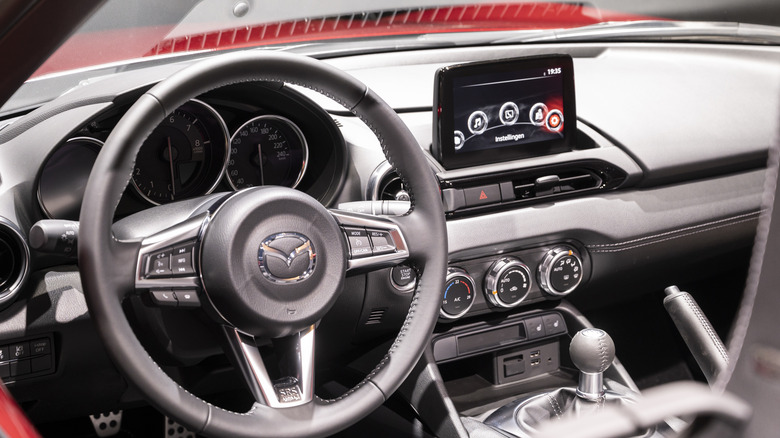
Anything that makes a car run more efficiently can save the driver money when it comes down to it. Simple maintenance of hard-working components like the spark plugs can help here, but with SkyActiv-G, Mazda is trying something more ambitious than that. This technology aims to ensure that the engine itself runs in a way that makes the best use possible of its fuel. Here's exactly what SkyActiv-G is and the science behind the concept.
The concept of Skyactiv-G
Since the very first vehicles with internal combustion engines (ICE) were developed, car-makers have been iterating upon them to make them more practical and more powerful. If this weren't the case, drivers might still be behind the wheel of Carl Benz's 0.75 hp Benz Patent Motor Car of the 1880s. SkyActiv-G represents Mazda's latest efforts to improve its fuel-powered vehicle performance further.
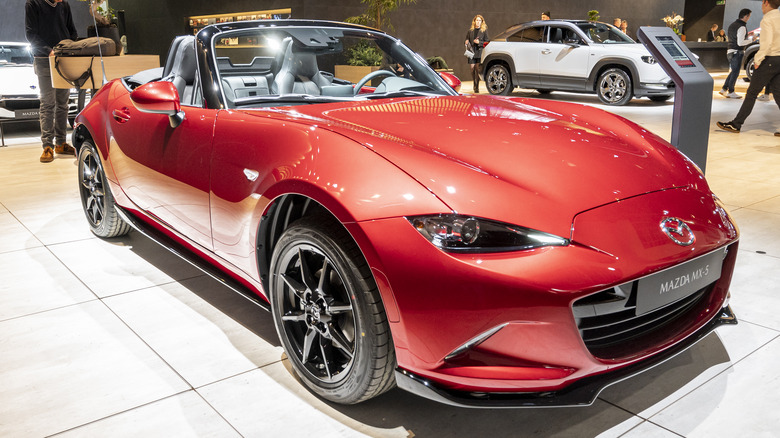
The SkyActiv-G is an ICE that boasts an engine compression of 14.0:1. This isn't just a super high level, Mazda boasts, but a world first. The company states that it offers 15% more torque and fuel efficiency than its previous engines. As AutoBlog reported in October 2010, the engine model changed its name from the original moniker of Sky-G (G for gas) around that time, and it was also joined by a diesel model, the Sky-D. In the United States, the SkyActiv-G's ratio is adjusted to 10:1 instead, but the engine remains unique.
Newer vehicles, such as the Mazda CX-30 (2024 model year), utilize a 2.5-liter model of the SkyActiv-G, which can hit around 320 lb-ft of torque and a potent 250 horsepower. Though bigger and more powerful engines can tend to be correspondingly hungrier (routine engine care, again, can help with this), the SkyActiv line aims to incorporate some interesting features to prevent this. Let's take a look at how the technology works.
How does the SkyActiv-G work?
Though Mazda credits the high engine compression of the SkyActiv-G as a primary reason for its improved performance, it's important to note that a level of 14.0:1 isn't, in and of itself, necessarily a positive thing.
A December 2021 study, "Numerical comparative study on knocking combustion of high compression ratio spark ignition engine fueled with methanol, ethanol, and methane based on detailed chemical kinetics," by Xiaoyan Li et al., addresses this. The authors note that while "[a] high compression ratio generates high thermal efficiency," it simultaneously "causes knocking combustion." Mazda's task in developing the SkyActiv-G was taking as much advantage of the former factor as possible while mitigating the latter.
Mazda uses a direct form of fuel injection, refining the process. The SkyActiv-G engine family also incorporates piston cavities, helping keep temperatures – and, in turn, engine operation – stable by separating the fire from other areas that could compromise the delicate heating and cooling balance. Uneven performance is a root cause of that dreaded knocking, after all.
A creative approach to maximizing fuel efficiency doesn't always pay off. In July 2019, CNET reported that a recall had to be issued on more than a quarter of a million Mazdas, as their cylinder deactivation systems could cause issues with engine functionality during the switch between modes. Even so, the SkyActiv range demonstrates that efficiency and innovation are going to be crucial considerations for manufacturers to take on as regulations on energy use evolve.