Why Porsche Loves The Flat-Six Engine (And Why You Should Too)
While electric vehicles are all the rage nowadays, internal combustion engines (ICE) can't be counted out entirely, especially among car enthusiasts — after all, gasoline power plants have come a long way since Carl Benz's first two-stroke vehicle spluttered and smoked its way across Germany in 1888 (via the Bertha Benz Memorial Route). While the principle of the matter hasn't changed much since that first motor, modern iterations of the ICE are far more efficient, lightweight, powerful, and varied in design.
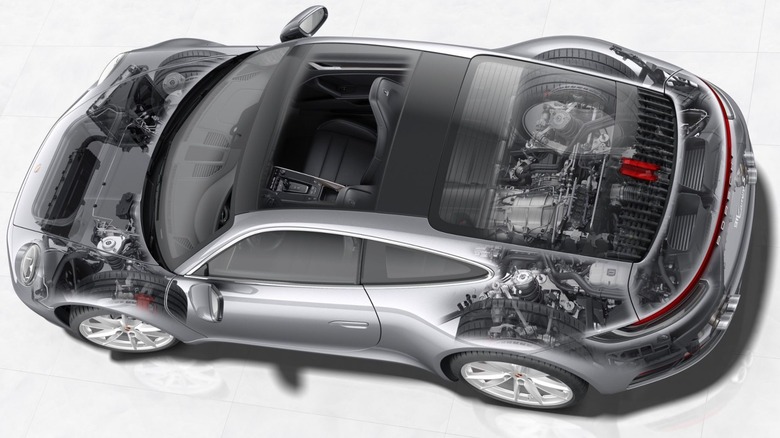
While the various manufacturers of traditional gasoline-powered engines have toyed around with impressive technologies to get a leg up on the competition — some less successful than others — most ICE motors have vertical or almost-vertical piston strokes with a combustion chamber located at the top of the piston's stroke. On the one hand, there are common alternatives, like the V and W configurations from makers like Ford and Bentley, which aim to optimize power output and simplicity while reducing weight and size. On the other hand, Porsche decided almost 60 years ago that it was going to go a different direction entirely, opting for the boxer engines that improve speed, efficiency, and packaging characteristics.
What is a flat-six engine?
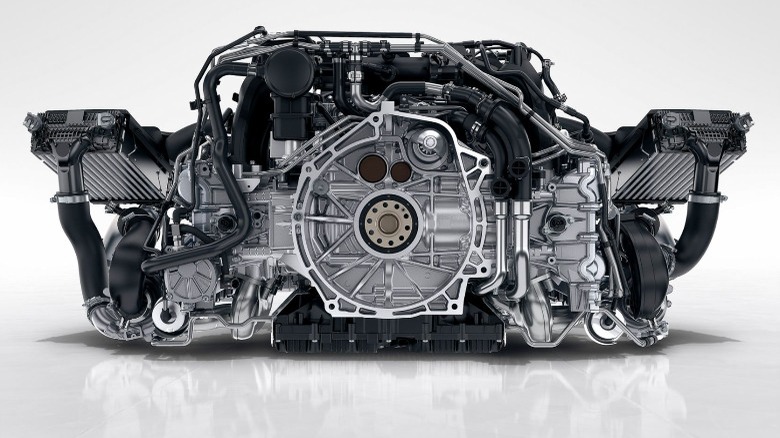
The flat engine (also called a boxer or contra engine) flips the script and pistons, opting to have a horizontal piston stroke, with the combustion chambers on either side of the crankshaft on the outer edge of the engine. Aside from the odd SUV, Porsche primarily designs and manufactures sports cars; generally, this means small, flat vehicles with mid- or rear-mounted engines. Since boxer engines have a horizontal stroke, they can be much lower profile than their inline- or v-configuration counterparts.
The compact size and unique profile of the flat-six engine mean more than just a smaller car: designers can also lower the center of gravity of their vehicles. A lower center of gravity makes a vehicle more stable on the road and helps drivers make snappier movements and get through corners at higher speeds without doing unintentional barrel rolls. In addition to a smaller package, flat-six engines can generally rev higher, run smoother, and operate more efficiently thanks to some unique technical aspects of the motor.
There's more to an engine than speed
The timing of the piston strokes in an engine can have knock-on effects on other components and end up drastically affecting the operating characteristics of the engine. Flat-six engine designs are simpler than inline-six or V6 configurations, because they're inherently better balanced, thanks to the opposing pistons balancing each other out.
In a V6 or inline-six engine, the crankshaft needs counterbalancing elements to help reduce free inertia and free moments — both features that reduce efficiency and cause rough running — which flat-six engines often forego without negative consequences. Porsche has spent so much time perfecting its flat-six engines that it's managed to reduce the free inertia and free moments to zero. The combination of a small, smooth-running engine and low center of gravity gives Porsche the ability to design more compact cars that handle better through the corners and have a better power-to-weight ratio than the competition, making them faster and more fun to drive.
The 2.7-liter flat-six engine earned Porsche its fourth "Engine of the Year Award" in 2013, according to Automotive World. Porsche made its decision regarding the flat-six engine over 50 years ago and has stuck with it since for good reason. The continued development of the design has led to an efficient, lightweight, high-performance motor that allows Porsche to achieve the rear-engine designs and driving characteristics it so desperately chases.