Windows 10 1903 Broke Chrome And Other Browsers' Secure Sandboxes
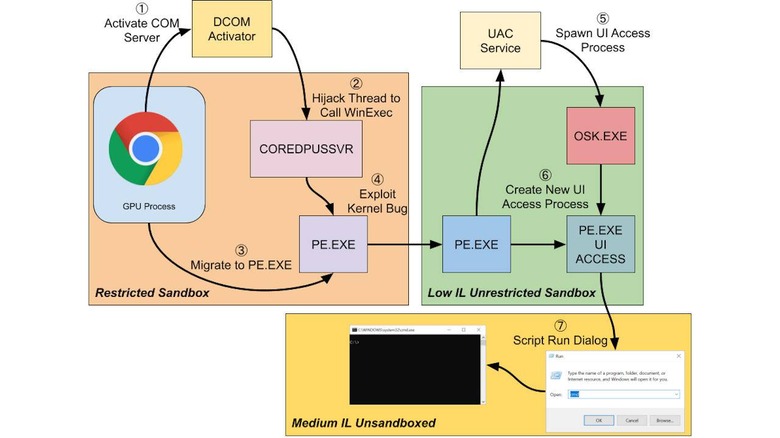
Web browsers have become very powerful but, as the cliché goes, that power also comes with responsibility. Major browsers like Chrome often use sandboxing methods to make sure that any wayward web page won't be able to harm the rest of the system. Those sandboxing methods, however, ultimately rely on the underlying operating system's capabilities and unfortunately for those that rely on Chromium's sandboxing on Windows 10, Microsoft changed just one line of code that rendered almost all major web browsers' sandboxes ineffective, including Chrome and, ironically, Microsoft Edge.
The basic principle behind sandboxing is to make sure that processes, in this case, the part of the browser processing web pages, have as little access to critical system resources as possible. That relies on the OS' facilities, which in Windows 10's case revolves around Restricted Tokens that were introduced way back in Windows 2000.
Unfortunately, a security researcher from Google's Project Zero bug-hunting effort came across a single change in a single line of code in the May 2020 Windows 10 update that changed the way these Tokens are handled. The researcher, James Forshaw, was able to try out several methods to prove how it was possible to break the Chromium sandbox on Windows 10 now.
One might presume that only Google's Chrome is affected by this bug but it actually affects almost all the popular browsers running on Windows are actually now vulnerable. That because many of them, including Google Chrome, Opera, Brave, and Microsoft's own Edge, actually use Chromium underneath. Ironically, Mozilla Firefox also uses Chromium's sandboxing at least on Windows which means it is affected as well.
Microsoft has yet to make any statement regarding this disclosure. The slightly good news is that the bug isn't exactly that easy to exploit without other OS-level vulnerabilities as well. Google's security researcher does point out, however, how such a small change on that level could cause many previously secure systems to come falling down.