Researchers Discover A Key Link To Autism Spectrum Disorders
Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan have discovered a new direct genetic link to autism spectrum disorders. The researcher's new study shows that the deficit in histone methylation could lead to autism spectrum disorders. A human variant of the SUV39H2 gene led researchers to examine the absence of that gene in mice.Study researchers found that when that gene was absent, adult mice exhibited cognitive inflexibility similar to what's seen in autism. When the gene was absent in embryonic mice, they had an improper expression of genes related to brain development. The study findings represent the first direct link between SUV39H2 and autism spectrum disorder.
Researchers note that genes are turned on and off during the development of humans, but genetic variation means that genes are turned off in some people but remain turned on in others. Gene expression is why some adults can digest dairy products while others are lactose intolerant. The gene that makes the enzyme lactase is turned off in some adults but not in others. Histone methylation is one of the processes the body uses to turn genes on and off.
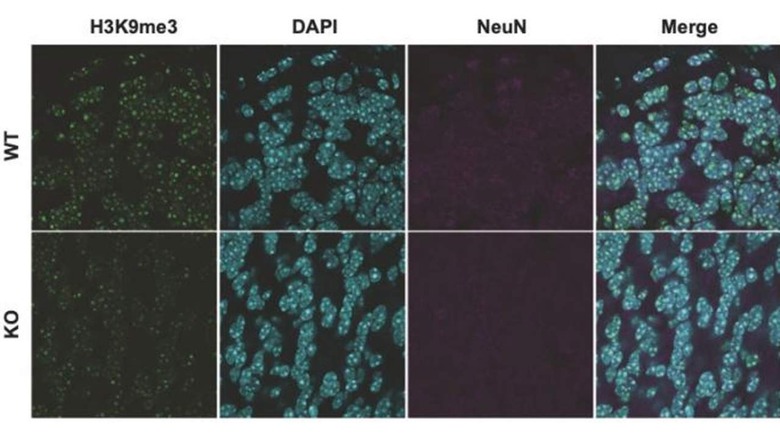
In histone methylation, special enzymes transfer methyl groups to histone proteins wrapped around DNA. Variation in genes related to methylation during brain development can lead to serious consequences. One of the variations is a rare disorder called Kleefstra Syndrome, where a mutation prevents methylation of H3K9, which is a specific location on histone H3. Kleefstra Syndrome resembles autism in some ways, so the researchers looked for autism-spectrum variations in genes able to modify H3K9.
Among nine of those genes capable of modifying H39K, the researchers found one variant, SUV39H2, was present in autism. The mutated SUV39H2 prevented methylation when tested in the lab. The team noticed a similar loss of function results for the mouse version of the variant. The research shows that activating the SUV39H2 gene is a potential therapy for mental disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, and requires more investigation studies.