New Dark Matter Map Relied On The Light From Millions Upon Millions Of Galaxies
It's hard for most of us to fathom that every star we see in the nighttime sky is another sun similar to our own. Scientists are discovering that around many of those stars are orbiting planets creating vast numbers of solar systems. There are other objects in the nighttime sky that we can't see, including dark matter.
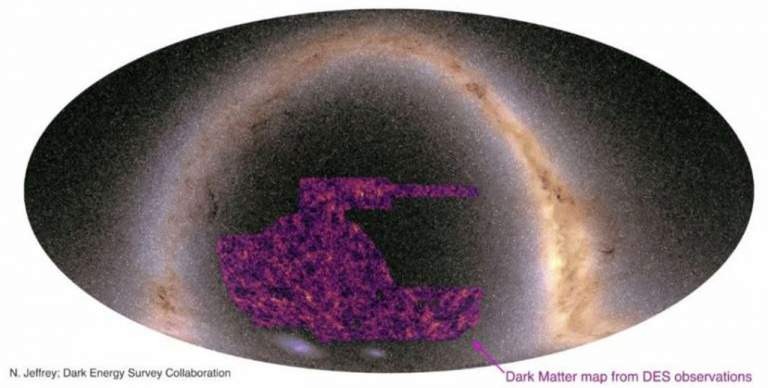
Dark matter is invisible and accounts for about 80 percent of the total matter in the universe. Scientists have been working hard for decades to learn as much as possible about dark matter and the role it plays in the universe as we know it. Scientists have now created the largest map of dark matter ever as part of the international Dark Energy Survey.
The team says it used AI methods to analyze images of 100 million galaxies, specifically looking at their shape to see if they had been stretched. Researchers on the project investigated spots of light made up of 10 or so pixels from the images to determine if they had been stretched at all. The new map represents all matter detected in the foreground of observed galaxies and covers about one-quarter of the sky as seen in the southern hemisphere.
Co-lead author of the study Dr. Niall Jeffrey says most of the matter in the universe is dark matter, and it's challenging to get a glimpse of that matter in the nighttime sky. Structures are revealed using the distorted shapes of hundreds of millions of distant galaxies. The map created by the team shows predominantly dark matter, and scientists found a pattern that is similar to what we see with visible matter.
The study revealed a web-like structure with dense clumps of matter separated by large empty voids. Dark matter has not been directly observed, and its existence can only be inferred from galaxies that behave in ways that aren't predicted. Scientists relied on gravitational lensing to create their map because it allows them to see visible and invisible matter. The team believes their study brings humanity closer to understanding what the universe is made of and how it evolves.