Scientists Research Why The Moon Is Rusting
Scientists are currently investigating why the surface of the moon is rusting. What baffles scientists so much is that there is no air or water on the moon, which are both required for hematite, which is a type of rust, to form. The new study looks at data gathered by the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 orbiter.
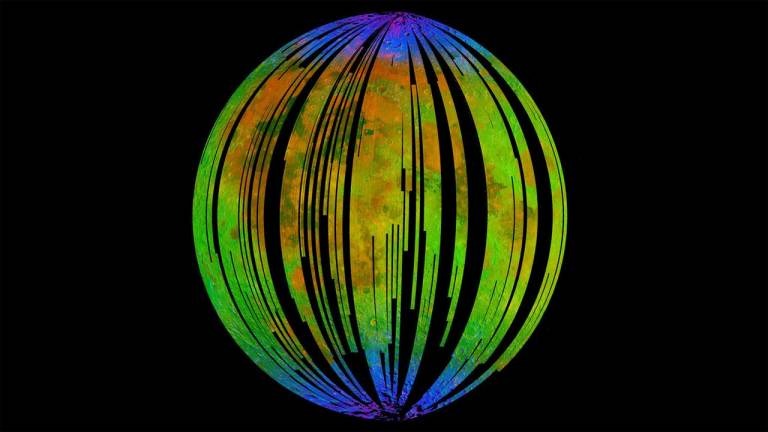
The orbiter discovered water ice on the Moon's surface and mapped various minerals while surveying the Moon's surface in 2008. The team looked over data gathered by the orbiter's Moon Mineralogy Mapper instrument built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Researchers say that water interacts with rock to produce a diversity of minerals. The orbiter's instruments detected spectra of light reflected off surfaces, which revealed that the moon's poles had a very different composition than the rest of it.
The moon's surface is littered with iron-rich rocks, and researchers were surprised to find a close match with the spectral signature of hematite. Scientists were surprised because the moon isn't supposed to have oxygen or liquid water to cause it to rust. Both the Moon and Earth are constantly hit by the solar wind, a stream of charged particles coming from the sun, that bombards both with hydrogen.
While researchers intend to continue studying why there is rust on the Moon, researchers from the University of Hawai'i have issued a separate study that outlines how they think Earth's oxygen may have caused rust on the moon for billions of years. Researchers from the University hypothesize that lunar hematite is formed through oxidation of lunar surface iron by the oxygen from Earth's upper atmosphere that has been continuously blown to the lunar surface by the solar wind.
They believe when the Moon was in the Earth's magnetotail over billions of years, oxygen leaving Earth hit its surface. Researchers also found that locations where hematite is present strongly correlated with water content at high latitudes. The discovery is reshaping our knowledge about the moon's polar regions and how Earth may have played an essential role in the evolution of its surface.