Android malware level triples in Q2 2012
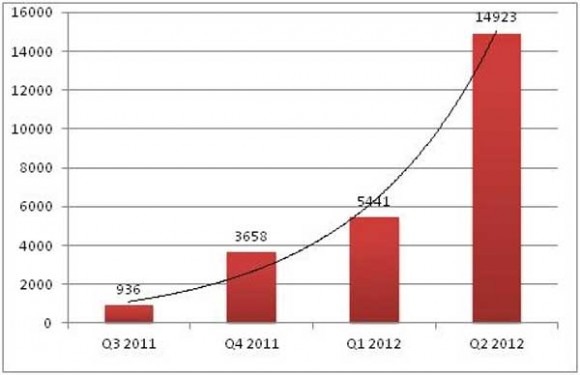
Anyone that uses a smartphone, tablet, or computer knows that there's a lot of malware out there with the goal of infiltrating your device and stealing information or causing you headaches. According to security company Kaspersky Labs the amount of malware out there specifically targeting Android increased by a significant amount in Q2 of 2012. The company reports that malware levels increased threefold during Q2.
Kaspersky reports that during the three-month quarter 14,900 new malicious programs targeting Android devices were added to its database. The massive increase in malware indicates according to the company that virus writers are increasingly targeting mobile devices with their malicious programs. It also clearly indicates that the growing popularity of Android is making it an ever-increasing target for nefarious programmers.
Kaspersky reports that 49% of the malicious files added to the database during the quarter were multi-functional Trojans that steal data from telephones such as contact names, e-mail addresses, and telephone numbers. These Trojans were also capable of downloading additional modules from servers run by the programmer. The security company reports that a quarter of the Android specific malware detected were SMS Trojans.
A SMS Trojan is a program that steals money from the victim by sending SMS messages to premium rate numbers without the user knowing. These programs are becoming more widespread and have been seen in 47 different countries whereas a few years ago they were limited to countries of the former USSR, Southeast Asia, and China. One of the most alarming statistics is that 18% of the Android threats detected during the quarter were back doors that could give malicious users full control over an infected device. This type of program is used to build botnets consisting of mobile devices. Trojan Spy programs made up 2% of the discovered malware and according to Kaspersky; this is the most threatening the users. This sort of malware transfer data to give the malicious user access to bank accounts.