Google seeks to control Android by making more apps closed source
When Google's Android operating system first started as an attempt to compete against Apple and the original iPhone Google really didn't have anything to lose. The iPhone was dominating the smartphone market at the time and the way Google decided to compete against Apple was offering a free smartphone operating system that it could sell ads on the and various applications to make money. It took a while to catch on, but eventually Android became the most popular smartphone operating system out there.
Offering a free and open-source operating system early on made sense for Google, but now that Android is the most popular operating system Google is reportedly trying hard to keep a tight grip on what started out as an open source operating system. The way Google is doing that is by bringing more and more applications, which are the lifeblood of any mobile operating system, under its closed source control.
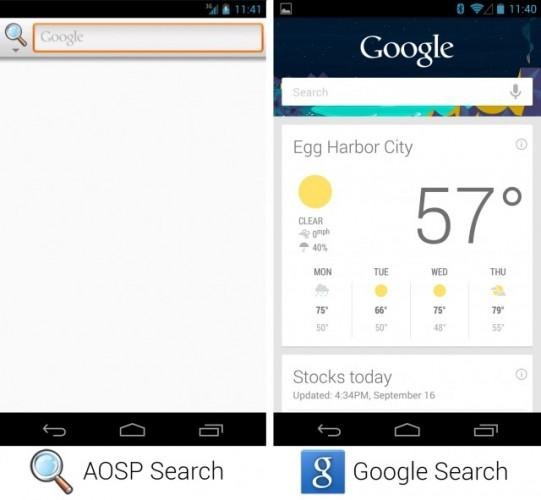
Some of the important applications for Android still have open-source equivalents, but for many once a closed source Google version of the app is launched on work on the open source version was halted. Since an open-source app really can't die, what Google did was simply move all of its development efforts to the new closed source version of the app.
As Google stopped developing open source code it means any competitor looking to make its own version of Android using open source code has to do more work putting more of the onus on the company and giving Google a bit more control over its operating system. One of the apps Google has moved closed source is the Search application, which has changed significantly. Google's proprietary version has all sorts of features while the open source version can only do web-based and local searches. Several other apps have gone proprietary as well including the Music app, calendar, Gallery and camera app and several others.
Another thing about the proprietary apps is that most of them are the stuff that smartphone manufacturers must have on their devices to be competitive such as Gmail, maps, Google now, hangouts, YouTube, and the Google Play Store. Since those apps are proprietary they have to be licensed from Google, which means manufacturers run the official version of Android. What that means is if a competing company were able to make their own popular version of Android it would be difficult to get smartphone manufacturers to adopt it because the in demand applications will require a license from Google.
SOURCE: Ars Technica
