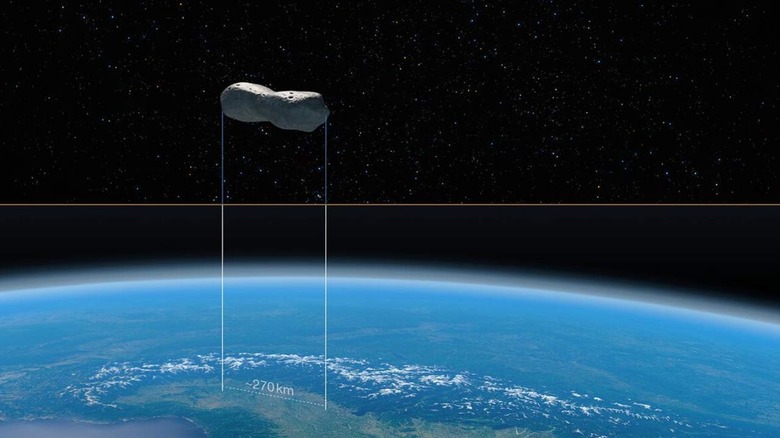
ESO images "dog bone" asteroid called Kleopatra in detail
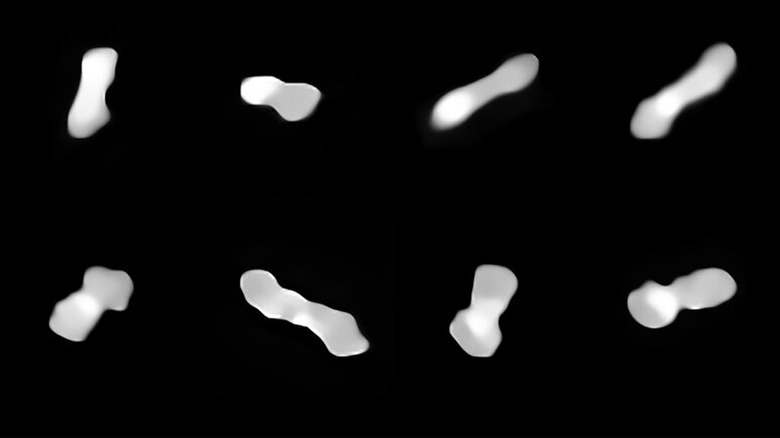
At the European Southern Observatory, Astronomers have leveraged the Very Large Telescope to take the most detailed images of a peculiar asteroid known as Kleopatra. The asteroid is shaped like a dog bone and is quite large at 270 kilometers. To put its size in perspective, 270 kilometers is roughly half the length of the English Channel.
Kleopatra orbits the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter in our solar system's Asteroid Belt. It's also been known as the "dog-bone asteroid" since it was discovered via radar observations two decades ago. It gets that name because the asteroid has two thicker ends that are joined by a thick neck. Another interesting fact about Kleopatra is that it has a pair of moons orbiting called AlexHelios and CleoSelene.
In an effort to learn more about the unique asteroid, the astronomers used images taken in 2017 and 2019 using the SPHERE instrument, which is part of the ESO VLT. The asteroid's rotation allowed the astronomers to view it from different angles, and the data was used to create the most accurate 3D renderings of Kleopatra so far. The asteroid was known to have its two orbiting moons, but a second study showed the moons didn't orbit where past data predicted them to be.
Discovering exactly where the two moons orbit is critical, with astronomer Miroslav Broz saying that if the orbits of the moons are wrong, other critical aspects about the asteroid could be wrong as well, including its mass. In the new study, the astronomers were able to gain precise data on how the asteroid's gravity affects the movement of those moons and discover their correct orbits.
With more accurate data on the complicated orbits of the two moons, researchers were able to recalculate the mass of the asteroid and found it was 35 percent less than past estimates. The team was also able to calculate new values for the asteroid's density, finding that it's less than half the density of iron which is less than previous estimates. That suggests a porous structure meaning the asteroid may be a large pile of rubble and likely formed following a massive impact.
