CRISPR-Cas9 modifies your DNA, under legal fire
A revolutionary method of editing the human genome has this week become the subject of a patent war. Back in April of 2014, patents were awarded by the USPTO (United States Patent and Trademark Office) to the Broad Institutes' Dr. Feng Zhang, MIT, and Harvard to develop the technology behind "CRISPR-Cas9". This April, the UC Board of Regents' legal team spoke with the USPTO about reconsidering their action, suggesting they award the patent to the inventor of the original method, UC Berkeley's Jennifer Doudna. One way or another, this radical DNA modifier must be made.We need X-Men, after all.
The following video will explain what this genome-editing piece of technological breakthrough is all about. CRISPR-Cas9 is what it's called, and getting in to your body to make changes on a DNA level is what it's going for.
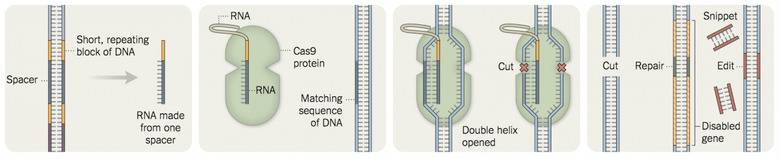
CRISPR-Cas9 works as a tiny scissors.
Utilizing the natural bacterial-level protective system used by your body to fight infections, CRISPR-Cas9 replicates the sequences of target DNA strands and latches on.
It's the connector that CRISPR-Cas9 makes real, and really programmable.
Your body provides the Cas9.* The Cas9 is the nuclease enzyme that cuts DNA strands.
*Correction – BACTERIA have Cas9, not our human selves. As helpful commenter "John" put so eloquently, "So far it has only been found in bacterial cells, and that's one of the things that makes it so amazing–a relatively simple molecular system that replicates many of the functions of our elaborate adaptive immune response, all in a single prokaryotic cell!"
ABOVE: Image comes via Nature; Addgene, By Jonathan Corum, via NYT.
When a DNA sequence is cut, it may attempt to re-form. In doing so, it can create mutations.
But that's a discussion for another day.
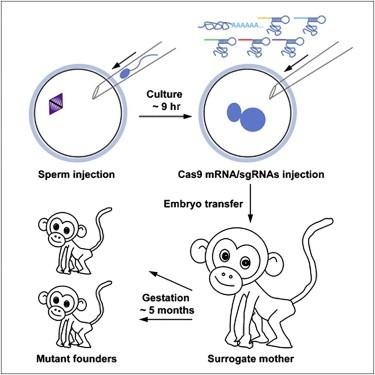
Genetically altered twin monkeys have been made using the CRISPR-Cas9 method. As you'll see in DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.027 in Cell Symposia "Generation of Gene-Modified Cynomolgus Monkey via Cas9/RNA-Mediated Gene Targeting in One-Cell Embryos", these monkeys are living large on gene-altered action.
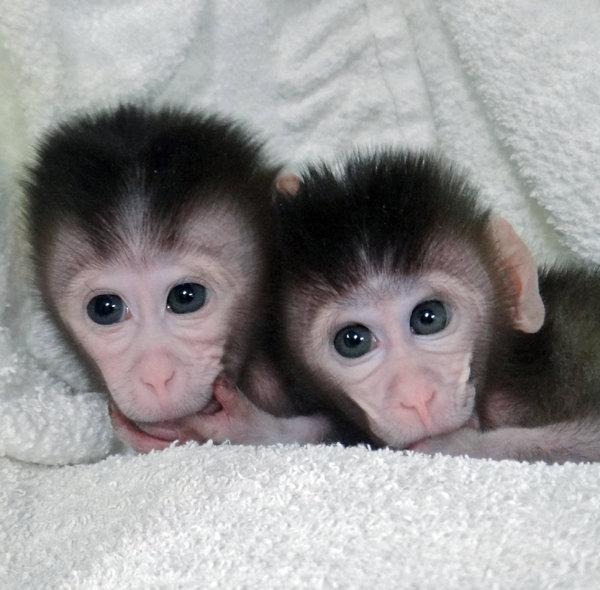

Today what's important is that two groups are fighting for the patents involved in CRISPR-Cas9.
A paper published online June 28 2012 by Science authored by Martin Jinek, Krzysztof Chylinski, Ines Fonfara, Michael Hauer, Jennifer A. Doudna, and Emmanuelle Charpentier describes the method: "A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity."
You can find this paper under code DOI: 10.1126/science.1225829.
Dr. Zhang suggests he demonstrated the CRISPR genome editing method before the 2012 paper was published by Dr. Doudna and Dr. Charpentier and crew. Dr. Doudna and Dr. Charpentier and crew suggest say Dr. Zhang's notebook (used as proof for patents) does not prove genome editing before the 2012 paper was published.
Can't we all just get along? Think of the monkeys!
